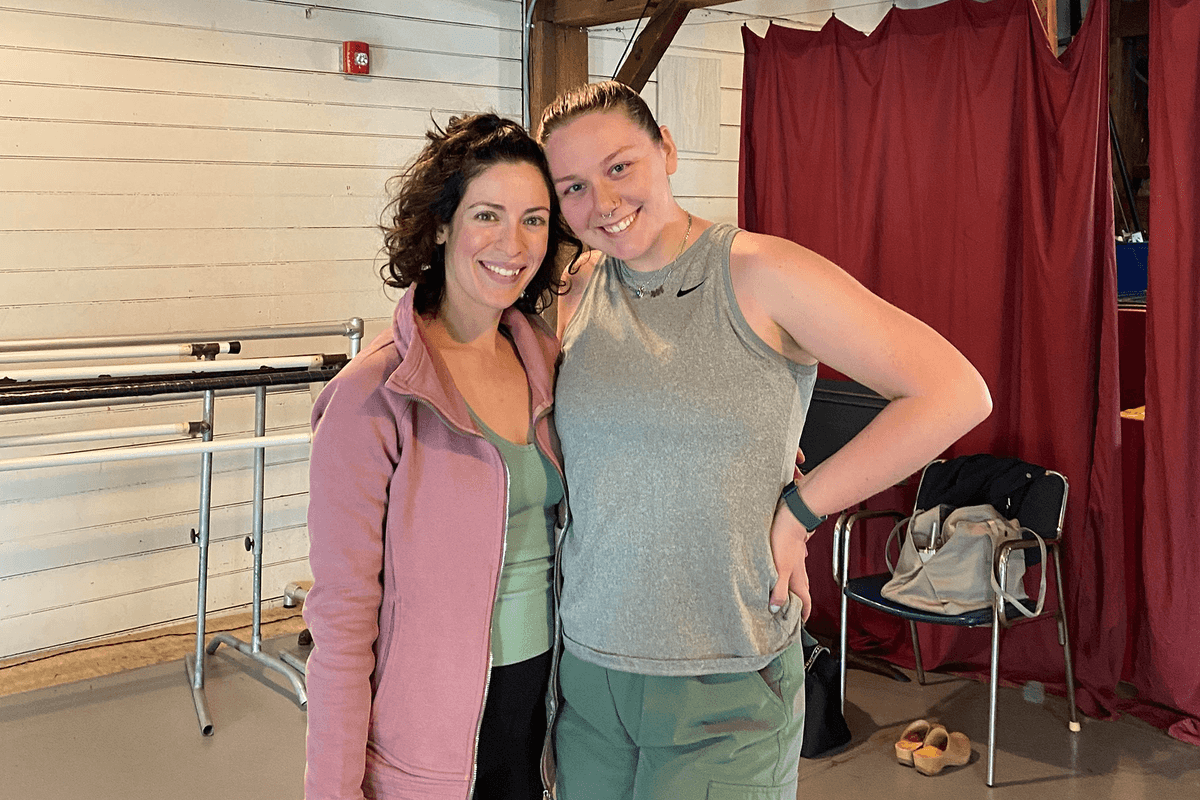Latest News
Cornwall signs contract for new fire trucks
Riley Klein
Mar 11, 2026
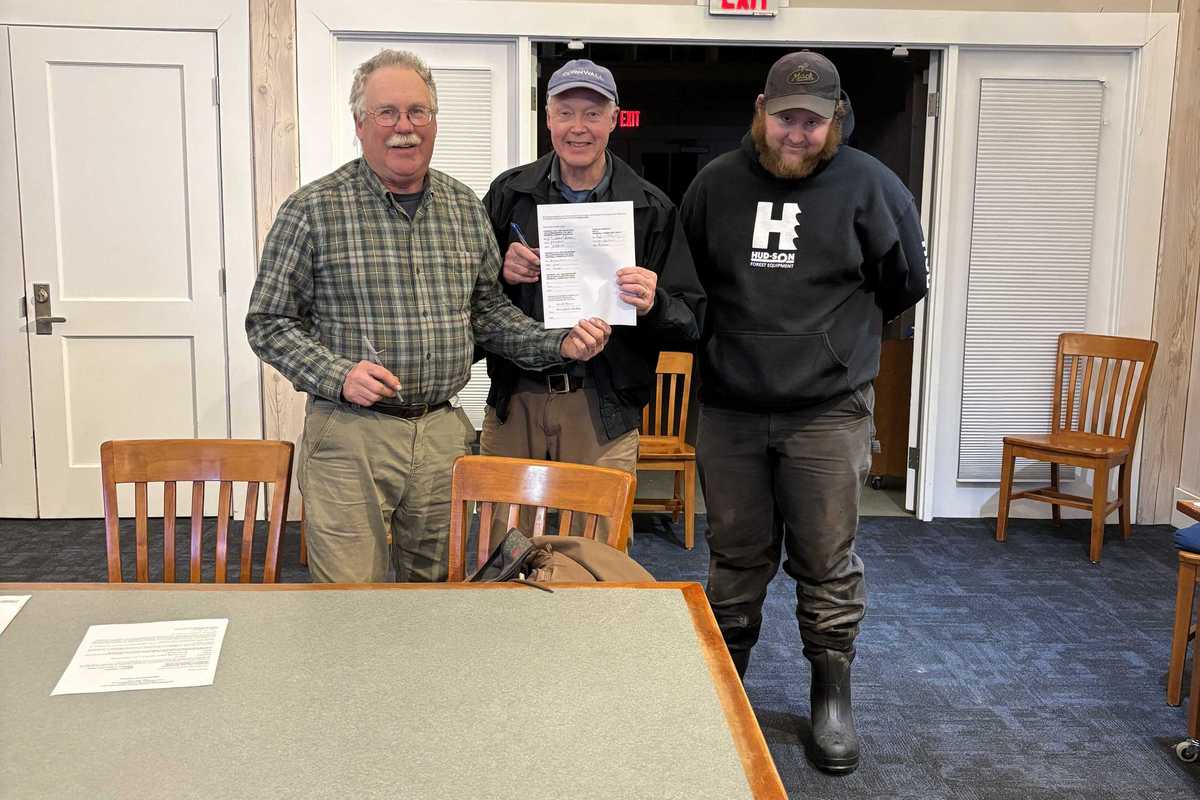
From left, is First Selectman Gordon Ridgway, Dick Sears and CVFD Chief Will Russ signed the contract for two new fire trucks March 3.
Provided
CORNWALL — Cornwall Volunteer Fire Department and the Board of Selectmen signed the contract for two new fire trucks Tuesday, March 3.
The custom rescue pumper and mini pumper will be manufactured by Greenwood Emergency Vehicles, located in North Attleboro, Massachusetts.
The cost is $1.2 million and the estimated delivery time is mid-2027. CVFD raised $600,000 in donations, which will be paired with money from the town’s truck fund.
Greenwood had the lowest price and fastest delivery time of the three manufacturers that submitted bids.
The new vehicles will replace outdated trucks that are both more than 25 years old.
Keep ReadingShow less
From students to owners at New Milford’s award-winning dance studio
Natalia Zukerman
Mar 11, 2026
Elizabeth Frabizzio and Zoe Czerenda, once both students at FineLine, are now co-owners.
Provided
For Elizabeth Frabizzio and Zoe Czerenda, the studios at FineLine Theatre Arts in New Milford, Connecticut hold a lifetime of memories. Both women grew up there, first as students, then as young teachers. Last September, they became the studio’s new owners.
The studio was founded in 2006 by Broadway veterans Elizabeth Parkinson and Scott Wise. Parkinson, a former principal with the Joffrey Ballet, and Wise, a Tony Award winner for “Jerome Robbins’ Broadway,” built the school on professional-level training paired with a strong sense of community. As they prepared to step back from running the school, they didn’t look far for successors. In September 2025, they handed the studio keys to two dancers who had come up through its ranks.
“It felt like the natural progression of my career,” Frabizzio said.
Frabizzio joined FineLine as one of its earliest students during her senior year of high school. Not long after graduating, the founders offered her a small class to teach.
“They gave me my first class as I was dabbling in the professional world and auditioning and performing,” she said.
Her career soon took her well beyond New Milford. She performed as an ensemble dancer in the Radio City Christmas Spectacular at Radio City Music Hall, with the modern dance company Momix, and appeared in Darren Aronofsky’s “Black Swan.”
Over time, teaching pulled her back toward the studio. About 10 years ago, after getting married, Frabizzio began gradually taking on administrative responsibilities and helping run the school behind the scenes.
Also a New Milford native, Czerenda began dancing at FineLine as a child and later joined the studio’s pre-professional repertory company, Artists in Motion. By age 15 she was assisting with classes.

Today, Czerenda and Frabizzio share the day-to-day work of running the studio. Their first school year as owners has come with a few surprises.
“It’s been kind of a wild ride,” Frabizzio said, laughing. She welcomed her second child last summer, just as the transition to ownership began.
“I’m so lucky that I have Zoe,” she said. “She’s an amazing partner. She kind of steered the ship and ran the show the first trimester of the year.”
While the leadership is new, the philosophy of the studio remains firmly rooted in what Parkinson and Wise built.
“I’m definitely preserving the technique and the passion that Elizabeth and Scott brought to FineLine,” Frabizzio said.
The founders’ Broadway backgrounds shaped the studio’s approach to training, emphasizing strong technical foundations for dancers of all levels.
“A solid technique is something that anybody would want, regardless of aspirations,” said Frabizzio. “If you want to be a professional or if you want to be a recreational dancer, it’s important to learn the right way.”
FineLine now serves more than 100 students ranging from age 3 through adults. Classes include ballet, tap, jazz, contemporary, lyrical, acrobatics and musical theatre, along with vocal performance and drama. The theatre program is led by Robin Frome, who also runs the Sherman Playhouse.

The studio recently received another sign of its local support, earning first place in Litchfield Magazine’s 2026 Readers’ Choice awards.
“We were really excited to come in first place,” Frabizzio said. “It’s so great for the area.”
At the same time, the new owners are mindful of how demanding dance culture can sometimes become.
“What I pulled from the professional world was how toxic it could be,” Frabizzio said. “I just want these kids to feel loved. I want them to feel empowered and to know that they are enough at any ability.”
For the past 15 years, Frabizzio has primarily taught children between the ages of 3 and 10 — often their first introduction to dance.
“I don’t take that role lightly, especially now that I’m a mom,” she said. “I know what those first impressions are and what they mean.”
Her goal is simple: “I want them to walk away with love and joy,” she said. “I want them to be excited to come to class.”
Accessibility is also part of the studio’s mission. This school year, FineLine awarded $23,000 in scholarships to students through an application process supported in part by community performances at the studio.
Looking ahead, FineLine will present its annual spring performance at the end of May, followed by its summer programs in July and August.
For Frabizzio and Czerenda, the studio’s next chapter is less about reinvention than stewardship.
“We’re really trying to preserve what they gave us,” Frabizzio said. “And that’s the love and the joy of dance.”
“Being an educator has been the greatest blessing of my life,” said Czerenda. “To be a safe space, a light of positivity or an outlet for these kids is what makes this experience so special. They teach me how to be a better educator and I like to think I help them become better humans as well as dancers and performers.”
Find out more and sign up for a class at finelinetheatrearts.com
Keep ReadingShow less
Lenore Mallett builds community at the Colonial
Sally Haver
Mar 11, 2026
Lenore Mallett at The Colonial Theatre.
Rebecca Bloomfield
On any given day in Salisbury or Lakeville, you might spot Lenore Mallett picking up dinner at LaBonne’s supermarket or chatting with neighbors. What many may not realize is that this same neighbor helping people find plumbers, foster dogs — even future spouses — is also helping revive the historic Colonial Theatre in North Canaan and quietly shaping community life across the Litchfield Hills.
Mallett is one of the driving forces behind the restoration and reopening of the more than 100-year-old Colonial Theatre, which she and members of the Fiorillo family purchased, renovated and reopened in 2023 as a community cultural hub serving North Canaan and the surrounding region.
That Mallett is a creative, entrepreneurial, energetic and successful professional is indisputable. Today she holds two almost full-time jobs. The first is as a top-rated sales executive at William Pitt Sotheby’s International Realty, where she connects clients to the “homes of their dreams.” The second is managing the Colonial Theatre.
“We took on the acquisition and renovation of what was once the town’s popular movie hub decades ago and reconfigured it for the benefit of the town and its surrounding communities,” Mallett said. “It was our intention to remake it into a cultural hub, one that could house a wide diversity of events with broad public appeal.”
“We figured a good way to start was to rent out small spaces within the building,” she added. “We loved helping young entrepreneurs, acting as a launching pad for their small businesses, and we kept the rent affordable. Initially we had a housewares store, a hair salon, a baker in the basement and a photographer on the second floor. They all flourished, outgrew their spaces and successfully moved on. For us, it was like baby birds leaving the nest.”
Today the Colonial Theatre continues to support community programs, including its largest tenant, Canaan Kids Art Space. The organization hosts an after-school club for children ages 6 to 10 and a summer program with four one-week sessions, providing families with a safe and creative environment where children can learn about many forms of art and create their own work. Organizers also maintain a policy that no child is turned away for lack of funds, working with families to ensure participation.

The Colonial’s space — encompassing a second-floor ballroom, a 120-seat theater and several smaller rooms — is highly versatile and can be reconfigured to accommodate a wide variety of events and audiences. The venue has hosted movie screenings and festivals, graduation and awards ceremonies, large family reunions, birthday parties, cultural festivals, arts and crafts fairs, educational workshops and literary events including book readings and author talks.
“The space is open for the community to use as they see fit,” Mallett said.
Mallett’s generosity of spirit is also reflected in her volunteer activities. When her children were younger, she became a reading tutor at their elementary school, helping more challenged readers catch up with the rest of the class. She was also the co-founder of ReGroup, a Stamford-based nonprofit that helped women successfully return to the workplace after taking “gap years” to raise families.
More recently, Mallett and her husband became partners in Robbie’s Community Market in Great Barrington, the eatery founded by Sheffield native Robbie Robles that opened last summer.
Most recently, the Colonial hosted the Falls Village and North Canaan historical societies’ George Washington Ball celebrating the 250th anniversary of George Washington’s birth.
Coming up is a movie series featuring notable films from the 1980s and 1990s, to be shown once or twice a month. Planned titles include “Back to the Future,” “Top Gun,” “Jurassic Park,” “The Princess Bride” and “Ferris Bueller’s Day Off.” More events are in development, Mallett said. Community members can follow announcements on the Colonial Theatre’s website, canaancolonial.com, or watch the theater’s marquee for upcoming programs.
Keep ReadingShow less

Want more of our stories on Google? Click here to make us a Preferred Source.
The Mozarts you don’t know at the Mahaiwe
Graham Corrigan
Mar 11, 2026
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Provided
For centuries, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart has overshadowed nearly everyone in classical music, including the talented musicians in his own family: his father Leopold, his sister Maria Anna Mozart and his son Franz Xaver Wolfgang Mozart who were all prolific composers and musicians in their own right.
On March 15, Great Barrington’s Mahaiwe Theater will explore the legacy of Mozart with its “Meet the Mozarts” concert. It’s mostly Amadeus — a quartet will perform the maestro’s “Piano Trio in B-flat, KV 502” and “Quartet in G minor, KV 478” — but the evening will feature works from both the elder and younger Mozarts.
“The story of Mozart is forever an enigma,” said Close Encounters with Music’s artistic director Yehuda Hanani. “It’s really a mystery. How did a man who, as a child, dazzled the royals of Europe end up in an unmarked grave?”
Leopold Mozart is best known for writing a foundational textbook on playing the violin. His catalog included church music, opera dances and symphonies, though much of it has been lost over time. Amadeus was his seventh child, and he served as the boy’s primary music teacher after the toddler began imitating the piano lessons taken by his older sister.
“Mozart’s father really made him what he was,” Hanani said. “He was a devoted pedagogue. He drilled him, and he corrected his early pieces. And then, of course, he was a great promoter. He created the legend.”
Mozart’s son, Franz Xaver Wolfgang, was born just four months before his famous father’s death. His musical education included lessons connected to such figures as Joseph Haydn and Antonio Salieri, and he socialized with contemporaries such as Franz Schubert and Robert Schumann. He was a renowned composer in his own right, “and he probably would have been much more acknowledged and known if not for his misfortune of being the son of a great genius,” Hanani added. Wolfgang would often perform his father’s work alongside his own. As his tombstone notes, “May the name of his father be his epitaph, as his veneration for him was the essence of his life.”
The Mahaiwe’s concert will feature a fourth Mozart: AI Mozart. “We are living in a very revolutionary technological, artistic, cultural time with AI, and it’s creating some kind of cultural crisis,” Hanani said. “So, we’re doing something a little whimsical, a little naughty and a little serious at the same time.” The three-minute piece uses Mozart’s existing oeuvre to create a composite work.
Hanani has mixed feelings. “If you compare [AI Mozart] to Leopold and Wolfgang Mozart, it’s not so bad. But next to the real Mozart, it’s full of clichés and platitudes, and it’s really drawing on something that was already there… There’s no spark in it.”
For more information and tickets, visit Mahaiwe.org
Keep ReadingShow less
Before the Oscars: watch it or skip it
Brian Gersten
Mar 11, 2026
Photo courtesy Los Angeles Times Photographic Collection/UCLA Library
With awards season upon us, it’s that familiar time of year when one might realize they have seen little to no buzzworthy films this past year. Perhaps you were too busy shoveling your driveway this February to catch “K-Pop Demon Hunter.” Or maybe, after realizing there are 469 known feature films featuring Frankenstein’s monster, you thought it untoward to see the latest iteration of “Frankenstein” by Guillermo del Toro before viewing the previous 468 installments.
Whatever the case may be, if you need some last-minute conversational guidance for your upcoming Oscar party, I am here to get you up to speed on some of the 2026 Academy Award nominees that are worth seeing — and worth skipping.
“One Battle After Another” — SEE IT
Arguably the best movie of the year and a film that reflects our contemporary American moment better than anything else. Watching “One Battle After Another” is like looking in a mirror — witnessing an oppressive white nationalist government (represented by a grotesque Sean Penn) attempting to thwart a coalition of resolute freedom fighters (led by Leonardo DiCaprio, Teyana Taylor, Chase Infiniti, Regina Hall and Benicio del Toro). It’s a 3½-hour revolutionary roller coaster with unexpected laugh-out-loud humor, capped off with one of the greatest chase scenes ever put on film. A must-see.
“F1”— SKIP IT
A 2½-hour formulaic car commercial with next to no redeeming qualities. I’d skip it faster than Brad Pitt driving a McLaren at 200 mph.
“Bugonia” — SEE IT (BUT EXPECT NIGHTMARES)
Emma Stone and Jesse Plemons are hauntingly terrific in this twisted kidnapping escapade. Plemons plays a gaunt conspiracy theorist who thinks our capitalist overlord (Stone) is an alien intent on destroying mankind and taking over the world. A brilliant take on the complexity of conspiracies, the film keeps you guessing until the very end about what’s true and what’s not.
“Hamnet” — SEE IT (BRING TISSUES)
A Shakespearean tale of love and loss. To call it a tearjerker would be an understatement. A powerful and instant classic.
“Sinners”— SEE IT (IF YOU LIKE HORROR FILMS)
The one film of the year where the buzz surrounding the project might outweigh its artistic ambitions. Racist white vampires terrorizing Black juke joint patrons in the Jim Crow South is as scary a horror premise as there is, and there’s loads of powerful symbolism at play. But at the end of the day, it felt like just another gory, gruesome horror movie. Loved the Buddy Guy cameo, though.
“Marty Supreme” — SEE IT
Whether you like Timothée Chalamet or not, his performance as the Trump-esque Marty Mauser — a professional pingpong player and hustler who will stop at nothing to achieve his goals — is an astute take on the affliction of American exceptionalism. With an anxiety-inducing pace and cadence we’ve come to expect from director Josh Safdie, the film is full of truly bizarre and memorable moments and characters.
“The Alabama Solution”— SEE IT
Pine Plains resident Andrew Jarecki takes viewers inside the Alabama state prison system in a documentary constructed almost entirely from cellphone footage covertly shot by prisoners. The conditions inside are utterly deplorable and completely shocking — resembling modern slavery more than rehabilitation. One struggles to make sense of the inhumanity and to come to terms with the fact that this is happening in America in 2026.
The 98th Oscars will take place Sunday, March 15, 2026, at 7 p.m. The ceremony will be hosted by Conan O’Brien and broadcast on ABC, with streaming available on Hulu.
Keep ReadingShow less
Berkshire Waldorf School updates “Little Women”
Mike Cobb
Mar 11, 2026
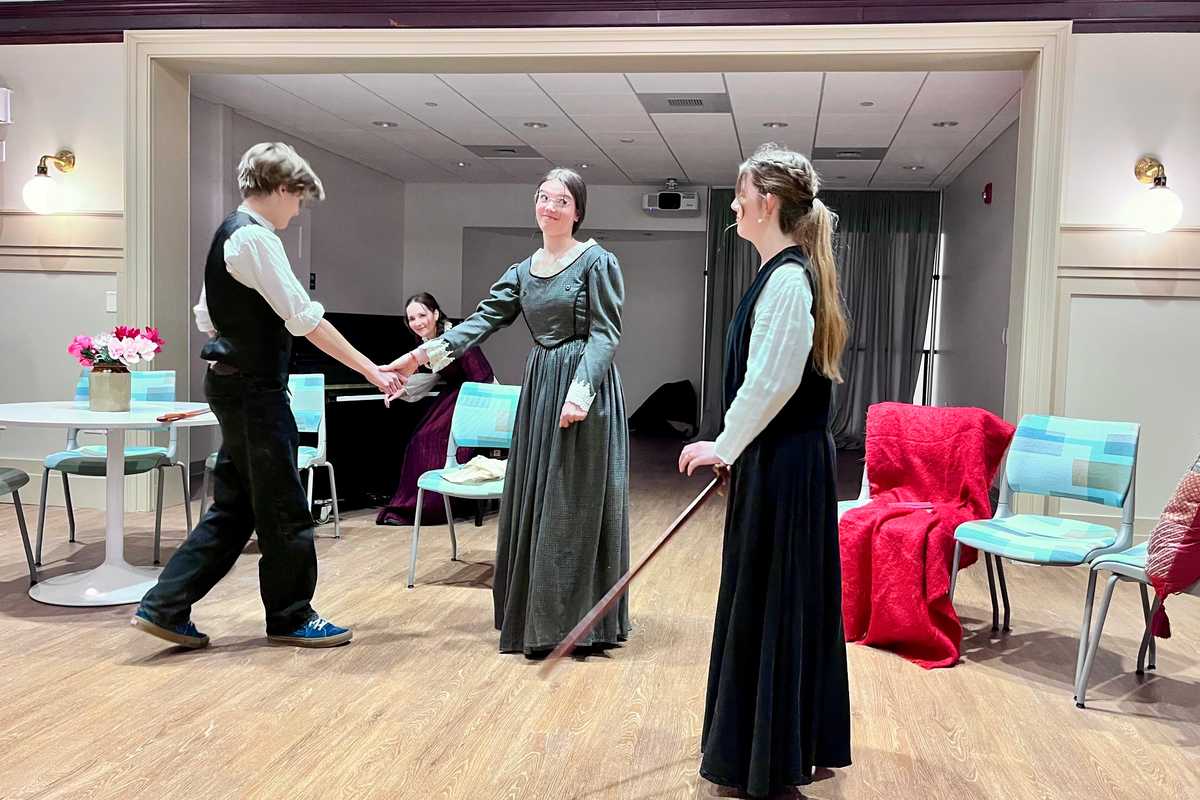
Students at Berkshire Waldorf High School rehearse for the performances of “Little Women” March 13-15 at The Unicorn Theater in Stockbridge.
Mike Cobb
The Berkshire Waldorf High School presents “Little Women” by Kate Hamill, adapted from the novel by Louisa May Alcott, at The Unicorn Theater in Stockbridge, Massachusetts.
Director Kendell Shaffer has taught screenwriting for the Writers Guild Foundation High School Screenwriting Workshops. About the choice of play, Shaffer said,
“The idea of ‘Little Women’ came from our senior girls who wanted a play with a heavy female cast after doing ‘The Outsiders’ last year. Kate Hamill’s adaptation is spunky, funny, with a contemporary feminist slant that transcends Louisa May Alcott’s ideas to today’s audience.”
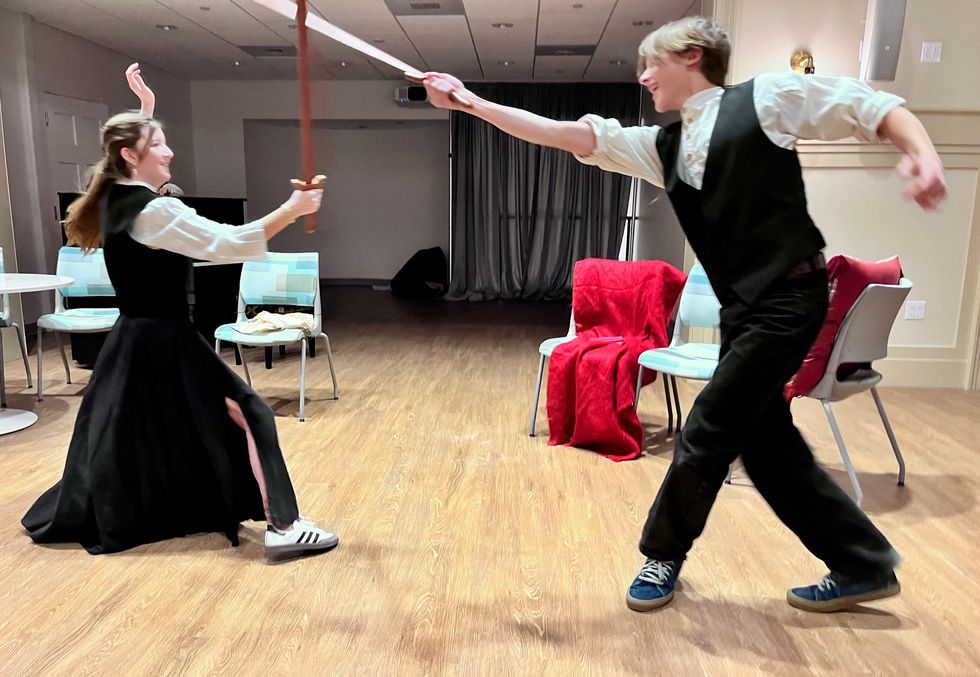

Actor Noelle Bodenstab said, “My role is Hannah. She’s very sassy and a very big contrast from the role I played in ‘The Outsiders’ last year. I feel as though it’s exercising my acting abilities, and I’m really excited to see how it turns out in the play.”
Actor Leo Martinez said, “I am playing Laurie, who is a friend of the Marches and this lonely, rich, sentimental guy who doesn’t really like the traditional idea of a man. His character revolves around his love for Jo, who doesn’t fit into the role of a girl very well, and them growing up together.”
The production features contemporary and original songs performed by the Berkshire Waldorf High School rock band.
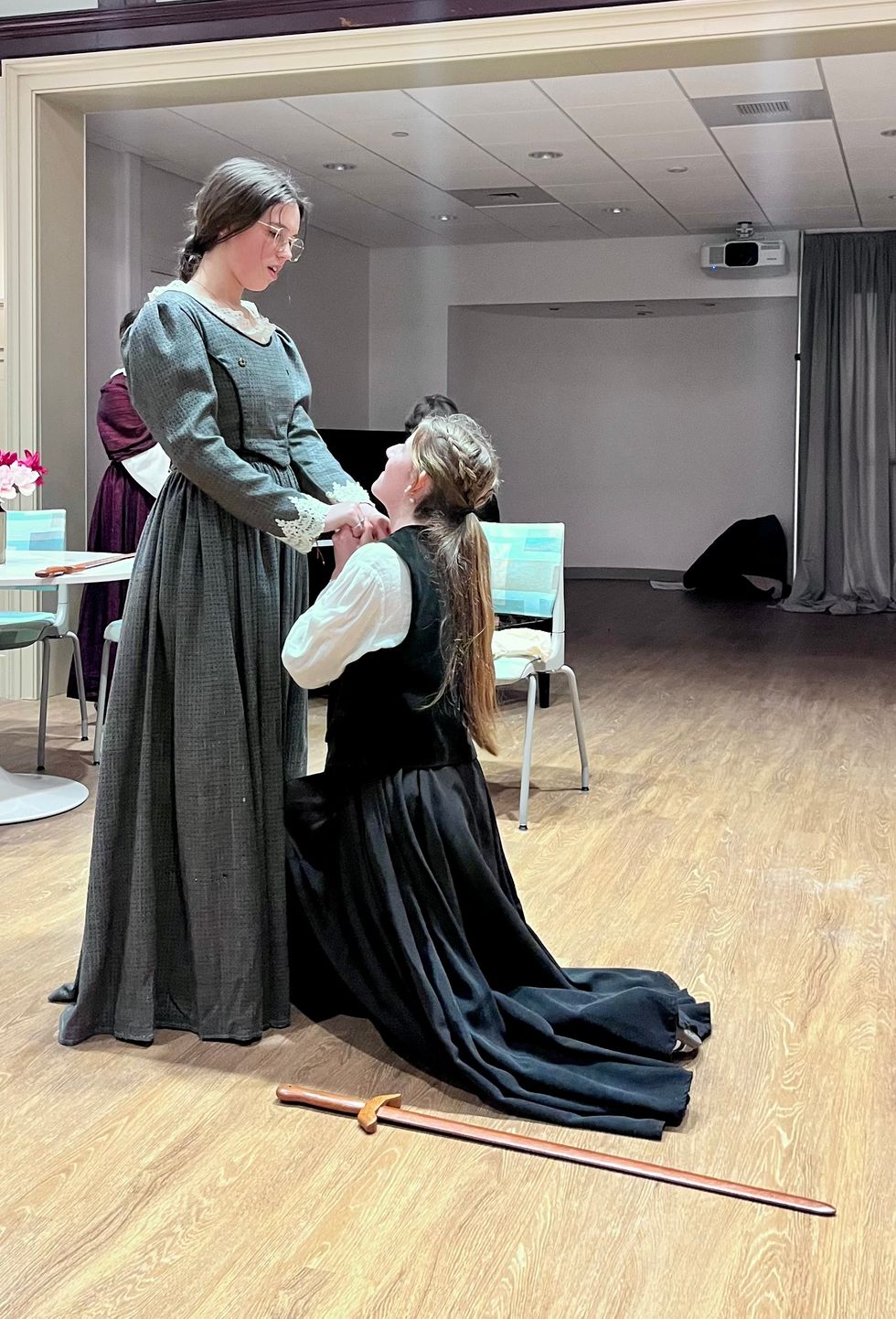

“Having been a TV producer in L.A. before relocating to the Berkshires, I like to add live music to plays I direct, similar to underscoring a film or TV episode,” said Shaffer. “The music helps guide the emotion and elevates the experience for both the audience and actors. Using contemporary music performed by our school’s rock band updates this classic play.”
“We are fortunate to have so many talented students at the Berkshire Waldorf High School and professional mentors working with the students as costume designer, choreographer, musical director, and vocal coach. The Berkshires are alive with artists, and it’s a gift to work with its seasoned and emerging talent,” Shaffer added.
Performances start at 7 p.m. Friday, March 13; 7 p.m. Saturday, March 14; and 2 p.m. Sunday, March 15.
For more information, visit berkshiretheatregroup.org.
Keep ReadingShow less

Want more of our stories on Google? Click here to make us a Preferred Source.
loading