Latest News
Club baseball at Fuessenich Park
Jul 09, 2025
Travel league baseball came to Torrington Thursday, June 26, when the Berkshire Bears Select Team played the Connecticut Moose 18U squad. The Moose won 6-4 in a back-and-forth game. Two players on the Bears play varsity ball at Housatonic Valley Regional High School: shortstop Anthony Foley and first baseman Wes Allyn. Foley went 1-for-3 at bat with an RBI in the game at Fuessenich Park.

Uncommon books at the intersection of art and literature.
Richard Kraft
Siglio Press is a small, independent publishing house based in Egremont, Massachusetts, known for producing “uncommon books at the intersection of art and literature.” Founded and run by editor and publisher Lisa Pearson, Siglio has, since 2008, designed books that challenge conventions of both form and content.
A visit to Pearson’s airy studio suggests uncommon work, to be sure. Each of four very large tables were covered with what looked to be thousands of miniature squares of inkjet-printed, kaleidoscopically colored pieces of paper. Another table was covered with dozens of book/illustration-size, abstracted images of deer, made up of colored dots. For the enchanted and the mystified, Pearson kindly explained that these pieces were to be collaged together as artworks by the artist Richard Kraft (a frequent contributor to the Siglio Press and Pearson’s husband). The works would be accompanied by writings by two poets, Elizabeth Zuba and Monica Torre, in an as-yet-to-be-named book, inspired by a found copy of a worn French children’s book from the 1930s called “Robin de Bois” (Robin Hood).
Pearson first encountered the world of alternative publications — magazines filled with experimental writing, artworks in the form of a book, and samizdat literature — as a young writer living in Berlin just before The Wall came down in 1989. Later, in New York City, she spent a great deal of time with artists “who were always making and assembling, whose continuous art-making made the thin membrane between art and life even more porous,” she explained.
Pearson traces the idea of publishing to a 2001 exhibition of artist-poet Joe Brainard. That show led to “The Nancy Book,” Siglio’s debut title in 2008, and she’s never looked back. The book contains over fifty full-page reproductions of Brainard’s dazzlingly accomplished and witty drawings of the cartoon strip character, Nancy. It includes essays and contributions by Robert Creeley, Ann Lauterbach, Frank O’Hara, Ron Padgett, and other poets of great renown, all thrilled to celebrate and remember Brainard (sometimes called “a poet’s artist”) who died of AIDS in 1994. Pearson said, ‘My first project with Brainard was such a good experience, I kept going. “
Since then, Pearson, the sole proprietor of Siglio, has designed, edited, and published over 40 books and other printed editions. Her books are characterized by unexpected juxtapositions of texts and images and collage-like assemblages, as well as for carefully designed and gorgeously printed volumes. Her list includes many “rediscoveries” of unpublished manuscripts and little-known publications. At the same time, she has commissioned new work from an impressive array of artists and writers such as Christian Marclay, Sophie Calle and Cecilia Vicinua among others.
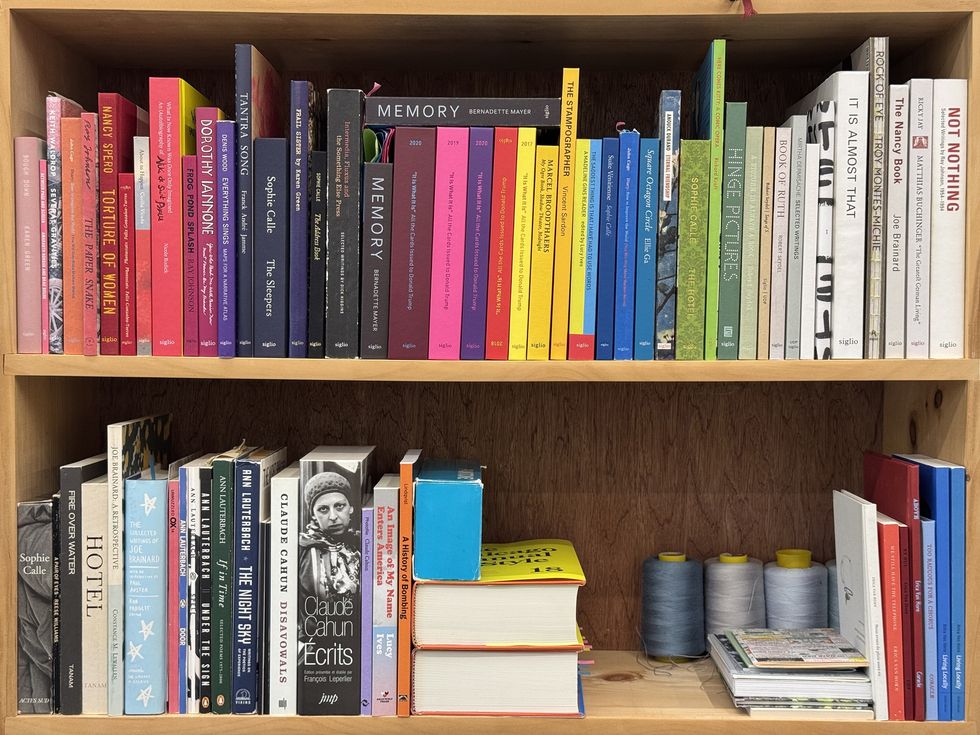

Though most Siglio books feature work by artists and writers from the 1960s to today, one standout— “Tantra Song” (2011) — showcases vibrant 17th-century Indian tantric paintings collected by poet-ethnographer Franck André Jammes, their modernist feel echoing Hilma af Klint or Brice Marden. Siglio also frequently draws on the spirit of the Fluxus movement, reissuing works by figures like John Cage and Ray Johnson with editions that honor their playful, ephemeral, and poetic origins.
Siglio also excels at photo-narratives rooted in highly specific, often eccentric concepts. “Memory” (2020), by avant-garde writer Bernadette Mayer, reproduces her journal and daily rolls of 35mm film from a month in the Berkshires in 1971, capturing the texture of each day. “Call and Response” (2022), created during COVID lockdown by composer and visual artist Christian Marclay, pairs his photographs of London’s quieted streets with musical scores composed in reply by his friend Bruce Beresford—each image in dialogue with sound.
Siglio books are sold through it’s website (sigliopress.com), as well as museum or specialty bookshops. (The Lenox Bookstore represents a number of Siglio books; the newly opened Lakeville Books & Stationery has copies of “Tantra Song.”) In all cases, Pearson strives to make “two or three degrees of connection” with each book buyer, including a “special gift” — often a piece of printed ephemera — with each purchase.
Keep ReadingShow less
Cyclists head south on the rail trail from Copake Falls.
Alec Linden
After a shaky start, summer has well and truly descended upon the Litchfield, Berkshire and Taconic hills, and there is no better way to get out and enjoy long-awaited good weather than on two wheels. Below, find a brief guide for those who feel the pull of the rail trail, but have yet to purchase their own ten-speed. Temporary rides are available in the tri-corner region, and their purveyors are eager to get residents of all ages, abilities and inclinations out into the open road (or bike path).
For those lucky enough to already possess their own bike, perhaps the routes described will inspire a new way to spend a Sunday afternoon. For more, visit lakevillejournal.com/tag/bike-route to check out two ride-guides from local cyclists that will appeal to enthusiasts of many levels looking for a varied trip through the region’s stunning summer scenery.
Where to rent and ride
Connecticut
Covered Bridge Electric Bike
Instagram @coveredbridgeebike
West Cornwall:
421 Sharon Goshen Turnpike
West Cornwall, Connecticut 06796
(860) 248-3010
Closed Tuesday, open 10 a.m. to 5 p.m. all other days
Kent:
25 N Main Street
Kent, Connecticut 06757
(860) 248-3010
Open Wednesday to Sunday,
10 a.m. to 5 p.m.
North Canaan:
1 Railroad Street
North Canaan, Connecticut 06018
(860) 248-3010
Open Wednesday to Sunday,
10 a.m. to 5 p.m.
With three locations in the Northwest Corner, this outfit offers a speedier way to zoom on two wheels through the hills with electric-powered offerings for sale or rent. Rentals are available for two hour trips, half days or full days, with several sizes and models in both throttle and pedal assist e-bikes of various styles. Route maps and e-bike trainings are on offer for renters, and guided tours are available on select weekdays. Visit the website, call or email at info@coveredbridgebike.com for pricing and more information.
Each location has its own suggested routes of varying difficulty. Ethan at the Kent location says, “The first place we send people is Macedonia Brook,” the shady and bucolic state park just northwest of downtown. For a more involved ride, Ethan also recommended the quiet country roads that wind through the picturesque hill valleys to the east of town, especially off of Kent Hollow Road and toward Lake Waramaug.
Spencer, who works at the newest location in North Canaan, said that a dual-state two hour ride that takes cyclists into Massachusetts in Ashley Falls, then down into Taconic on Barnum Street and back to North Canaan via Twin Lakes Road and Cooper Hill Road, is his favorite. At the company’s West Cornwall location next to the its namesake bridge, Spencer said a classic ride is up River Road all the way to Falls Village, where riders may visit Great Falls or find some refreshment at the soon-to-open Off the Trail Café. For a longer journey, Spencer suggested continuing up Housatonic River Road north from Falls Village, where it turns into dirt and passes through gorgeous riverside farm country.
New York
The Music Cellar
Instagram @the_music_cellar
14 Main Street
Millerton, New York 12546
(860) 806-1442
Scheduling is available via call or text 24/7
The Music Cellar is an all-instrument music school for aspiring instrumentalists, but it also rents beach cruiser bikes during the warmer months. “They’re perfect for the rail trail,” says owner and music instructor Johnny, referring to the currently 26-mile (and expanding) bike and footpath that passes just outside the storefront. “You don’t have to worry about hitting little bumps or potholes or curbs or whatever – they’re good all-purpose bikes,” he said.
Unique among area bike rentals, the Cellar offers rates starting at $20 for those looking for a shorter ride up to $50 for the day and Johnny said that he’s happy to accommodate sliding scale pricing for locals might have trouble affording the full rate. “It does help keep the lights on, though,” he said, “so if you’re renting bikes, you’re helping kids learn music!”
Johnny said that with the Harlem Valley Rail Trail at his front doorstep, he usually sends riders for a journey on the reclaimed abandoned railbed. The path currently stretches from Wassaic to the hinterlands of Hillsdale, with another 20 miles to Chatham planned to be built in the next five years pending funding. Johnny said riders can choose to head north for sweeping valley vistas below the Taconic mountains, or, “for a more shady ride, you could go south – also equally scenic, lots of wildlife. You can go all the way to Wassaic Station and jump on a train to New York.”
Bash Bish Bicycle & Tour Co.
Instagram @bashbishbicycles
247 NY-344
Copake Falls, New York 12517
(518) 329-4962
Tuesday to Saturday, 10 a.m. to 5 p.m.; Sunday 10 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Located a dozen or so miles up the rail trail is the “ye olde bike shop of the Hudson Valley,” as described by its owner Sam. The shop is just two years from its 30th birthday, and appropriately exudes small-town charm without skimping on modern equipment and service. “It’s the best little bike store in the Hudson Valley,” said Northeast resident Dan Sternberg, who was clad in a cycling kit outside the store on a sunny Friday afternoon in June.
The shop is situated steps from the rail trail, just below the deep, clear and refreshing water of Ore Pit Pond in Taconic State Park, a short jaunt from the old Copake Iron Works site and a mere half mile from the parking lot for one of the Taconic’s region’s treasures and the store’s namesake – Bash Bish Falls. Sam offers day tours to highlight the richness of the region – not only in its natural resources but also the pastoral, cultivated splendor of the farm roads that cut through the hills to the west of Route 22.
Sam says he plans to start running multi-day tours, drawing on experience he had guiding extending bike excursions while operating a lodge in Colorado. Also upcoming is a pop-up shop in Millerton for the summer, which he anticipates opening shortly once the permitting is in order.
In addition to tours, the shop offers sales, repairs and rentals, starting at $35 for a two-hour hybrid bike session ($15 for kids) and $45 for two hours on an e-bike. Visit the website for full pricing details on four hour, full day, multi-day, and weekly rates. Bookings can be made online or via phone.
Sam says he likes to direct guests towards the scattered gems of restaurants, bars and shops that pepper the rail trail corridor and into the hills and dales beyond. The Copake General Store, dishing coffee and café fare alongside locally-produced provisions is just down the road, while market and cultural center Random Harvest and beloved seafood peddler Zinnia’s Dinette sit a close ride away in Craryville. For a summer afternoon tipple, Roe Jan Brewing Company is up the rail trail in Hillsdale, and the creek-side beer garden atmosphere of the Lantern Inn is a somewhat stouter 25 miles down the path in the other direction.
Massachusetts
Berkshire Bike & Board
Instagram @berkshirebikeandboard
29 State Road
Great Barrington, Massachusetts 01230
(413) 528-5555
Monday to Friday, 10 a.m. to 6 p.m.; Saturday closing at 5 p.m.
and Sunday at 4 p.m.
With Berkshire locations in Great Barrington and Pittsfield, and two other satellites in Hudson, New York and Bloomfield, Connecticut, Berkshire Bike & Board offers the gamut of cycling needs – a wide variety of gear, expert sales assistance, service and repairs, and of course, rentals.
All four locations carry an e-bike, which costs $69.99 for a single-day rate or a discounted price of 49.99 for longer rentals. The Great Barrington store also offers a non-electrified gravel bike for a single day rate of $99.99 or $79.99 for multiple days. All bookings for rentals are made online on the company’s website.
Great Barrington employee Wyatt described the gravel bike as “a little more aggressive” than a standard hybrid, and “able to handle packed dirt, a little bit of loose gravel, back roads, but not be super slow like a mountain bike” on pavement.
He said both the e-bikes and gravel bikes are well suited to handle one of his favorite routes, the Alford Loop. An approximately 20 mile ride, cyclists take Alford Road northwest out of Great Barrington, and then upon reaching Alford, may choose to take East Road to West Road or vice versa for a scenic and easy circle through the Berkshire forest and fields. In Wyatt’s words: “Great loop, super quiet, not a lot of cars.”
Keep ReadingShow less
loading