Latest News
Wake Robin Inn sold after nearly two years of land-use battles
Christian Murray
Feb 21, 2026
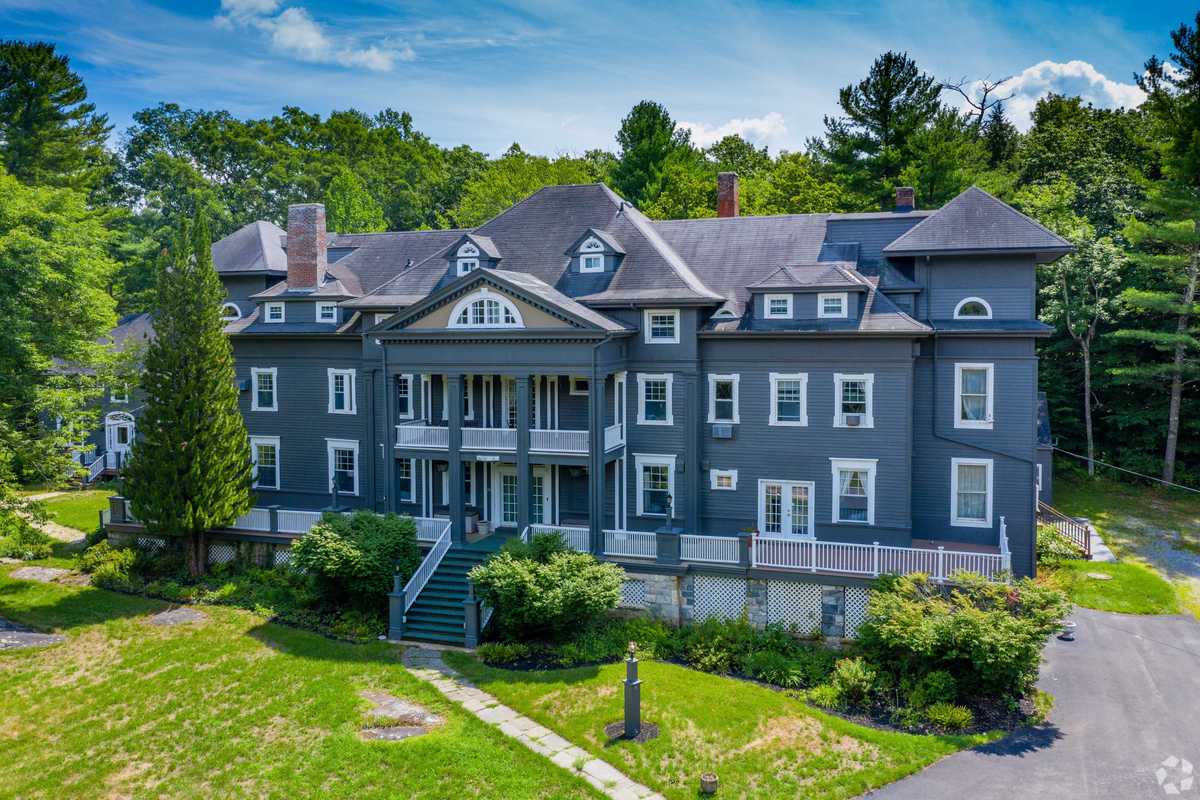
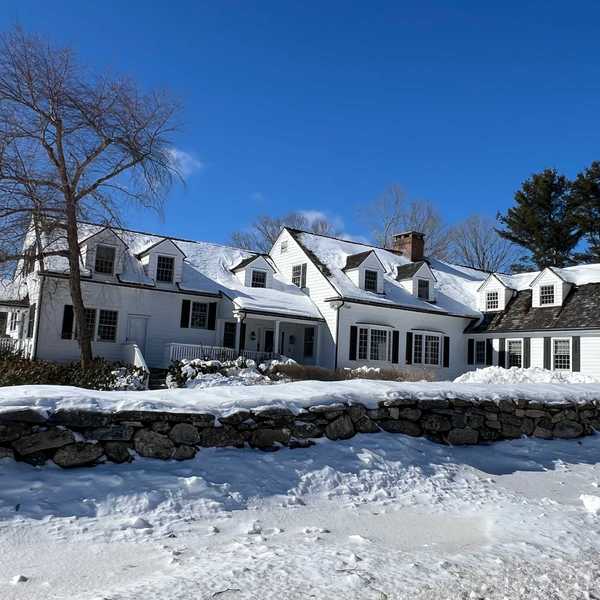
The Wake Robin Inn in Lakeville has been sold for $3.5 million following nearly two years of land-use disputes and litigation over its proposed redevelopment.
Photo courtesy of Houlihan Lawrence Commercial Real Estate
LAKEVILLE — The Wake Robin Inn, the historic country property at the center of a contentious land-use battle for nearly two years, has been sold for $3.5 million.
The 11.52-acre hilltop property was purchased by Aradev LLC, a hospitality investment firm planning a major redevelopment of the 15,800-square-foot inn. The sale was announced Friday by Houlihan Lawrence Commercial, which represented the seller, Wake Robin LLC.
Tom Cervone of CR Properties Group brokered the deal for Aradev.
Representatives of CR Properties and Aradev could not be reached for comment. Terms of the transaction, including whether the closing was contingent on the previously granted special permit or pending litigation, were not disclosed.
Long known as a wedding and retreat destination, the inn is slated to be transformed into what Aradev has described as a boutique hospitality campus serving Salisbury and the surrounding region.
Under the redevelopment plan approved by the Salisbury Planning and Zoning Commission in October 2025, the number of guest rooms would increase from 38 to 54. The project also includes a 2,000-square-foot detached cabin, expanded event space, a sit-down restaurant and fast-casual counter, as well as a spa, library, lounge, gym and seasonal pool.
The commission voted 4–1 to grant a special permit after seven public hearing sessions, adopting a nine-page resolution with 40 conditions. The proposal had been scaled back from an earlier version, eliminating a detached event barn.
Despite the approval, neighborhood opposition has remained strong. Wells Hill Road residents Angela and William Cruger filed two lawsuits challenging both an underlying zoning change and the redevelopment approval.
In late January, a Connecticut Superior Court judge in Torrington dismissed the couple’s lawsuit alleging that a 2024 zoning amendment allowing hotel development in the Rural Residential 1 zone where the inn is located was illegal “spot zoning” designed specifically to benefit the Wake Robin project. The court found the plaintiffs failed to demonstrate that public notice of the regulation was procedurally deficient.
When adopted, the amendment drew scrutiny from opponents who argued it had been crafted to advance the Wake Robin redevelopment. Town officials and land-use staff maintained the change was part of a broader effort to address longstanding nonconformities affecting historic inns across Salisbury.
A second lawsuit — an appeal of the commission’s approval of the redevelopment plan — remains pending.
Keep ReadingShow less
Kent commission tackles Lane Street zoning snag
Alec Linden
Feb 20, 2026
Lane Street warehouse conversion raises zoning concerns in Kent
By Alec Linden
KENT — The Planning and Zoning Commission is working to untangle a long-standing zoning complication affecting John and Diane Degnan’s Lane Street property as the couple seeks approval to convert an old warehouse into a residence and establish a four-unit rental building at the front of the site.
During the commission’s Feb. 12 meeting, Planning and Zoning attorney Michael Ziska described the situation as a “quagmire,” tracing the issue to a variance granted by the Zoning Board of Appeals roughly 45 years ago that has complicated the property’s use ever since.
The Degnans’ attorney, Jay Klein, initially appeared before the commission late last year with a proposal to amend the zoning regulations to accommodate the project. Commissioners and Ziska, however, expressed reservations about rewriting the regulations for a single property.
In the months that followed, Ziska and Klein worked together to identify an alternative path forward. They ultimately found one in Regulation 9320.4 of the town’s zoning code, which permits a nonconforming use to be changed to another nonconforming use, provided the new use is no more detrimental to the neighborhood’s character.
Under the revised proposal, the warehouse would be converted into a residence, and the four-unit building at the front of the property would be approved for residential rental use. Commissioners responded favorably to the approach, as did several neighbors who spoke in support. Residents noted that the plan would permanently eliminate the possibility of the warehouse returning to industrial or commercial use.
Over the years, the building has housed an auto body shop, an aquarium store, a sign production facility and other commercial operations.
The commission voted to keep the public hearing open until its March meeting to allow for additional discussion.
Keep ReadingShow less
Kent P&Z closes High Watch hearing, continues deliberations
Alec Linden
Feb 19, 2026
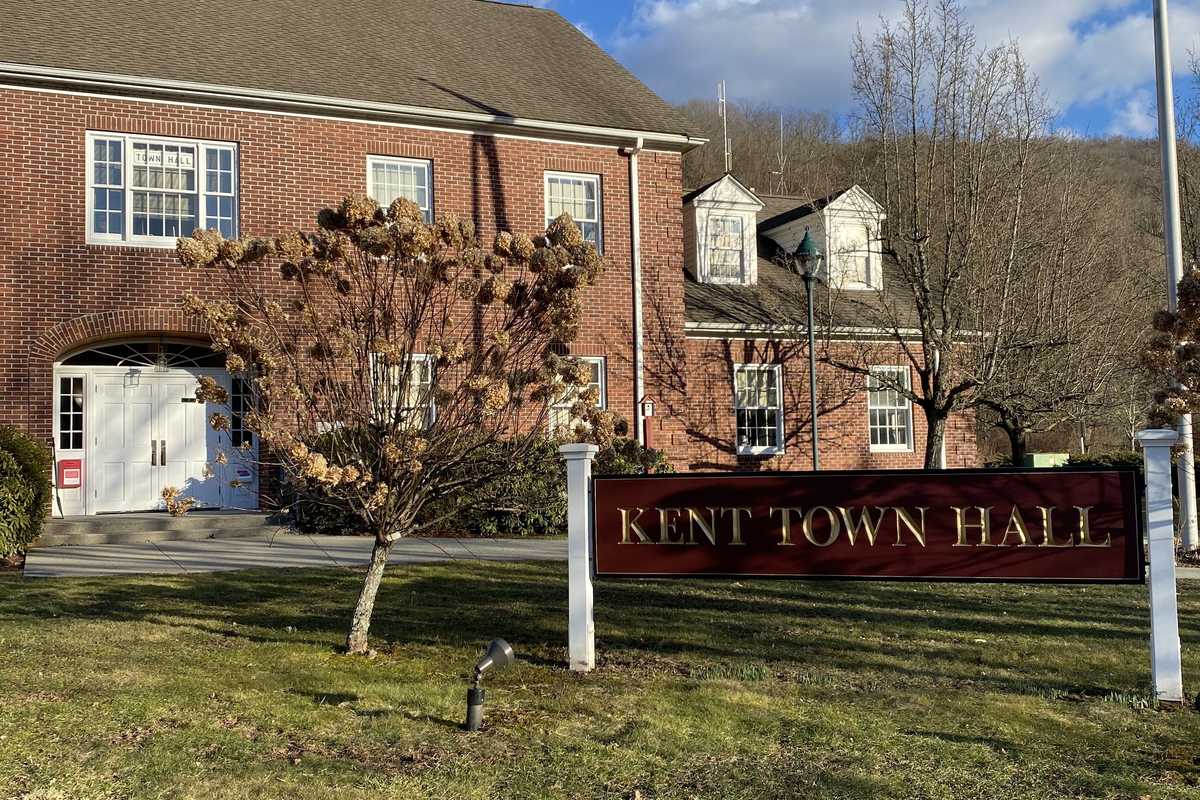
Kent Town Hall, where the Planning and Zoning Commission closed a public hearing on High Watch Recovery Center’s permit modification request on Feb. 12
Leila Hawken
KENT — The Planning and Zoning Commission on Feb. 12 closed a long-running public hearing on High Watch Recovery Center’s application to modify its special permit and will continue deliberations at its March meeting.
The application seeks to amend several conditions attached to the addiction treatment facility’s original 2019 permit. High Watch CEO Andrew Roberts, who first presented the proposal to P&Z in November, said the changes are intended to address issues stemming from what he described during last week's hearing as “clumsily written conditions.”
Neighbors have argued throughout the extended hearings that the proposed revisions amount to an undue expansion of the recovery center on rural Carter Road.
Among the changes originally proposed — but since withdrawn — was the addition of two beds to the detox unit. Another withdrawn proposal would have removed a rule barring the facility from admitting people in police custody or those ordered by a court to undergo treatment. Additionally, High Watch has withdrawn its request to eliminate the requirement that local officials be notified if a client leaves the campus without authorization.
The application still seeks to allow the facility to accept patients outside regular hours under unusual circumstances, while preserving P&Z’s authority to enforce standard admission hours if deemed necessary. The most controversial remaining request is the creation of a lecture hall for “staff education” that may include speakers and guests from outside the organization.
Despite the modifications, neighbors continue to voice objections.
Jeremiah O’Brien, whose property abuts High Watch, said he believes the organization has gradually exceeded prior limits.
“It’s been, if we give an inch they take a mile,” O’Brien said at the hearing, referencing what he described as past transgressions by the nonprofit, including the cutting down of trees years ago above Kent Falls.
Roberts apologized for any past wrongdoing and said his appearance before P&Z with the application is an effort to right past wrongs.
Karen Altfest, a Carter Road resident, described the management of the rehab center as “disingenuous” and the facility as “not a good neighbor.”
Annette Koberlein-James said the organization has grown beyond what she expected for the area.
“Nobody on this road bought their home to live next to such an ever-expanding, growth-focused organization,” she said. She acknowledged that the facility seeks to provide quality services and good jobs but added that “it has reached a tipping point that’s very real.”
Other residents offered a more supportive perspective. Lili Mason pointed to initiatives that have benefited the community, including Wilson’s Café on Main Street, which was established by the organization, and a vaccine clinic High Watch opened during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“It’s no longer the little place on the hill, which was adorable and sweet,” she said, “but is it really infringing that much on the neighbors?”
Ziska said the modified application generally reflects his recommendations but emphasized that P&Z is under no legal obligation to amend the original conditions and may accept or reject the request as it sees fit.
Keep ReadingShow less

Want more of our stories on Google? Click here to make us a Preferred Source.
Kent committee to review Swift House options
Alec Linden
Feb 19, 2026
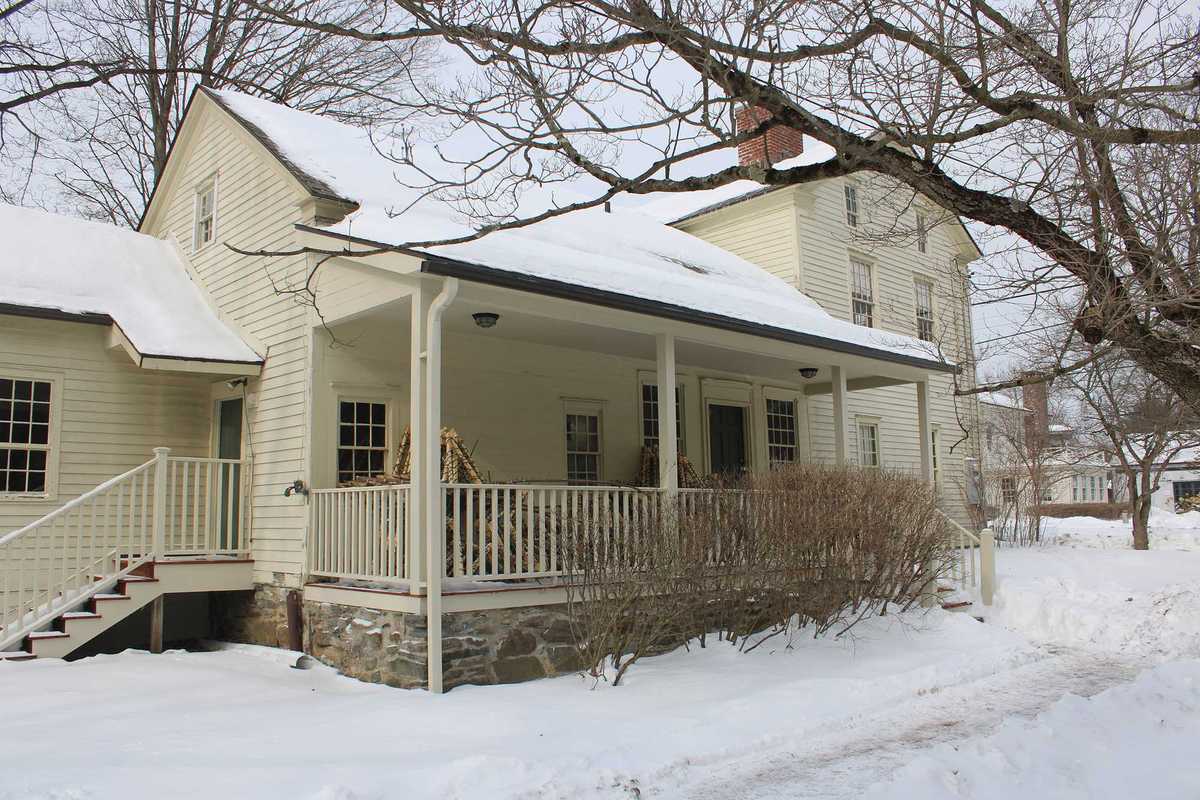
The Swift House in Kent has been closed to the public since the COVID-19 pandemic. A newly appointed town committee will review renovation costs and future options for the historic property.
Alec Linden
KENT — Town officials have formed a seven-member committee to determine the future of the shuttered, town-owned Swift House, launching what could become a pivotal decision about whether Kent should invest in the historic property — or divest from it altogether.
The Board of Selectmen made the appointments on Wednesday, Feb. 11, following recent budget discussions in which the building’s costs and long-term viability were raised.
The Swift House has been closed to the public since the COVID-19 pandemic. Its future has sparked debate among residents, with some viewing the property as a taxpayer burden requiring costly upgrades and others considering it a distinctive community asset central to Kent’s character and history.
Selectman Lynn Harrington will represent the BOS on the newly formed Swift House Investigation Committee. Jason Wright was appointed as the representative from the Board of Finance.
Five members of the public were also named to the panel: William Reihl, Margie Austell, Jim Anderson, Chris Adams and Marge Smith.
Anderson serves on the Historic District Commission. Adams is the newly appointed director of the Kent Historical Society, and Smith is the organization’s former director and current curator. The Historical Society is exploring the possibility of placing the Swift House on the National Register of Historic Places.
The committee has been charged with evaluating renovation and upgrade options — including costs associated with bringing the building into compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act — and determining what it would take to return the property to active use.
The panel will also examine options for selling or otherwise transferring the property out of public ownership should the town decide to divest.
The committee must present its findings by April 30, a deadline intended to allow potential budget adjustments ahead of Kent’s May budget hearing and vote.
Keep ReadingShow less
Kathleen Rosier
Lakeville Journal
Feb 18, 2026
CANAAN — Kathleen Rosier, 92, of Ashley Falls Massachusetts, passed away peacefully with her children at her bedside on Feb. 5, at Fairview Commons Nursing Home in Great Barrington, Massachusetts.
Kathleen was born on Oct. 31,1933, in East Canaan to Carlton and Carrie Nott.
Kathleen retired from Housatonic Curtain Company where she was a machine operator for many years.
She was predeceased by her husband of 65 years, John A.Rosier Sr., her son John A Rosier Jr., her son Frank H. Rosier and her brother Jerome Nott.
Kathleen leaves behind her son, Brian Rosier and his wife JoEllen of East Canaan, her daughter, Theresa Morin of Ashley Falls, her daughter, Lisa Dawson of Great Barrington, a brother Henry Nott, her sister Ann Percy, 11 grandchildren, nine great grandchildren and many nieces, nephews and friends.
There will be a celebration of life held in her honor on Feb. 21 from 1 to 4 p.m. at the Bitterman Center in North Canaan. All are welcome to come.
Keep ReadingShow less
Carolyn G. McCarthy
Lakeville Journal
Feb 18, 2026
LAKEVILLE — Carolyn G. McCarthy, 88, a long time resident of Indian Mountain Road, passed away peacefully at home on Feb. 7, 2026.
She was born on Sept. 8, 1937, in Hollis, New York. She was the youngest daughter of the late William James and Ruth Anderson Gedge of Indian Mountain Road.
Carolyn’s first job out of high school was at the Time and Life building in Manhattan, New York. In 1956, she went on to work for Capital Airlines until they disbanded.
She began banking in White Plains, New York, where she met her husband Edward James McCarthy. They started their family and relocated to Pleasant Valley, New York. She then returned to banking in Poughkeepsie, New York and later pursued real estate.
Carolyn was very creative and enjoyed home making, gardening, sewing, knitting, cooking and baking. Her Christmas cookies were always remarkable. She had a pioneer spirit and embraced the toil of yard chores. She was very independent and at 87 she still shoveled the driveway in the winter, mowed the grass, trimmed the bushes, raked the leaves and dragged the brush. She took pride in the manicure of the grounds where she resided.
Carolyn was a wonderful mother who had an enormous heart. She loved all animals, wild or tame. She will be dearly missed by her family and the people that knew her.
She is predeceased by her husband Edward McCarthy Sr. and her brother Dr. Stafford Gedge of Minnesota.
She is survived by her son, Edward (Anne) McCarthy of Greenfield, Massachusetts, and grandsons James and Theodore, son Sean McCarthy of Oak Hill, New York, sister Nancy Dougherty of South Carolina, nieces Lynn Warner, Debra Phillips, Susan Nelson, Christine Richards and nephews William, James and Robert Gedge.
A private service will be held at a later date.
The Kenny Funeral Home has care of arrangements.
Keep ReadingShow less

Want more of our stories on Google? Click here to make us a Preferred Source.
loading