Latest News
Thanks To You, Our Recent Donors
Lakeville Journal
Mar 02, 2026
Your contributions over the last year have made delivering trusted, local news possible.
Listed are donors who generously made a gift to The Lakeville Journal and The Millerton News between January 1, 2025 through January 31, 2026*
Anonymous (2)
21st Century Fund
Mike Abram & Vivian Garfein
Janet Accardo
Ceely Ackerman & Bert Schmitz
Susan Addison
Sandy Adelsberg
Ellen & Moshe Adler
Cameron Afzal & Lisa Straus
Peter & Alice Alderman
Michelle Alfandari & Tom Goldenberg
John & Susan Allen
Jennifer Almquist
American Online Giving Foundation, Inc.
Joan Amsler & Clyde Cathcart
Barry & Marilyn Anderson
Oscar Anderson
Janet Andre Block
Sally Andre
Steven Aresty
Judith Ascah
Scott Asen
Michael & Abby Auerbach
Mimi & Fritz Babcock
Jennie Baird & Christophe Armero
Peter & Margaret Bakker
Kristen Balderston
Jerry & Mary Ellen Baldwin
Harding Bancroft
Susan Bang
Barr Foundation
Andrea Barnet & Kit White
Bill & Maureen Barton
Bates Foundation
John Baumgardner
Kathleen & Richard Beatty
Justin Beeber
Aimee Bell
Bonnie Bellow & Frank Handelman
Karyn & Charles Bendit
Stephen Bennett
Douglas Benson & Paul Dassenko
Shereen & Steve Berger
Robert Berk
Berkshire Mountain Distillers
Berkshire Taconic Community Foundation
Ann Berman & Daniel Feld
Mina Bernhard
Barbara Bevington & Robert Fiengo
Robert & Nancy Bird
Block Family Foundation
Richard & Freya Block
Henry Blodget
Parker Boal
Paul & Mary Boghossian
Grant Bogle
Jeffrey & Tina Bolton
Anne Bowen
Robert L. Boyett
Pamela Boynton
Donald Brant, Jr.
John Brett & Jane Strong
Daniel Briggs
David & Joan Bright
Alden & Marianne Briscoe
John Brockelman
Julian Brod
Rick Brooks
Louise & Malcolm Brown
Louis Bucceri
Robert Buccino
Thomas Bucelwicz
Gladys Bucove
Churchill Building
Mark Bunnell & Julie Trager
Barbara Burge
Georgia Burger
Diana Burroughs
Nancy Bushnell
Jeannette Byers
Karen Byers & Lillie A. Mikesell
Renee & Geb Byers
Wheaton Byers
Blake & Elizabeth Cabot
Camilla Campbell
Sandra Canning
Jane & Mark Capecelatro
Peter & Cynthia Carberry
Jane Carlen
Thomas K. Carley & Alissa Churchill
Claire Carlson
Deborah & John Carter
Robert W. Casey, Jr.
Carl Chaiet & Lynn Kearcher
Lisa & Eric Chamberlain
John & Kristina S. Chandler
Heather Chapman
John & Sharon Charde
Devereux Chatillon
Anne Childs
Hope Childs
R.W. Ciferri III
Betsy Clark
James H. Clark & Jennifer Kronholm Clark
Kathleen Clarke
John & Anne Coffin
Joel & Terry Cohen
Erica Cohn & Jon Zucker
Barbara & Lee Collins
J. Barclay Collins & Kristina Durr
Dave Colmar
John Colpitts
Larry Conklin
Matthew & Catherine Connole
Anthony & Marjorie Consolini
Hilary Cooper & Chris Crowley
Cream Hill Foundation
Judith Crouch & Malcolm McKenzie
Ellen & Carl Culbreth
JP Cunningham
Wendy Curtis
Estelina Dallett
Hope Dana & John Perkins
Jody & Lee Davies
Anne Day & Spencer Reiss
Luisa De Castro
Lee & Sophia deBoer
Fredrick Deknatel & Emily McGoldrick
Susan DeMelle
Peter Demy
Leslie Denniston Hastings & Don Hastings
Mary DePasquale
Donna & James DiMartino
DJ McManus Foundation, Inc.
Carole Dmytryshak
John Doar Foundation
Francesca & Michael Donner
Maureen & Patrick Dore
Margaret Douglas-Hamilton
Caroline Downey
Meg & Ed Downey
Noreen Doyle
Jill & Derek Drew
Geoffrey & Daphne Drury
Anatoly & Nina Dubitsky
Michael Duca & Jackie Blombach
Gila Ducat Lipton
Laurie & Dary Dunham
Catherine & David Durning
Steve Dutton & Valerie Feuer
Dalton & Roshy Dwyer
Dan Dwyer & James Montanari
Lorna & Daniel Edmundson
Ian Edwards
Joanne Elliot
Michael Elliston & Roberta Gardner
Helen Ellsworth Scoville
Priscilla Ellsworth
Nancy & John Elting
John & Cyd Emmons
Angela Engle
Joel Ernst
John & Linda Estabrook
Mimi Estes
Jonathan Ezrow
George & Lorraine Faison
Duggan Family
The Potter Family
Rosemary Farnsworth
Juliette Feeney-Timsit
Richard Feiner
Peter Felske & MR Halle
Laurie Fendrich & Peter Plagens
Milton Ferguson
Eileen Fielding
Karl Filippini
Robert Fish
Peter Fitting
Molly & Frank Fitzmaurice
Meghan Force
Pari Forood
Foundation for Community Health
Eileen Fox & Henry Rosler
Sam Fraidin
Debra & Barry Frank
Sherry & Bruce Frankel
David Freeman & Ellen Kunes
Mary Elizabeth Freeman
Ingrid Freidenbergs
Carole Bailey French & John French
Katherine Freygang
K. Evan Friedman & Susan Knight
Joseph Frydl
Judy & Leo Gafney
Christopher & Miriam Galligan
Scot Galliher
Jean Gallup
Tino & Susan Galluzzo
Jane Garmey
Bruce Garner
Perry & Susan Gasperini
Martin Gavin
George T. Whalen, Jr. Foundation
Joe & Phyllis Geraghty
Karin Gerstel
Albert Ginouves
Amy Glickman & Andrew Kuritzkes
Marilyn & GB Godsoe
Ann Gold
Michael Goldman & Jill Choder
Jonathan & Harriet Goldstein
Elizabeth & Charles Goodyear
Michael Gordon
Benjamin Gott
Bobby Graham & Matt Marden
Kate Green
Kim & Jeff Greenberg
David & Rita Greene
Edward & Diana Greene
Gwen Greene
Laurie Greene
Rachel Greenfield Minkoff & Ronald Minkoff
Lee Greenhouse & Flora Lazar
Edith Greenwood
Nan Greenwood
William and Mary Greve Foundation
Marilyn Gross & Kim Hausner
Stephen Gudernatch
Licia Hahn
Bob & Sandy Haiko
Helen Haje
Peter & Amanda Halle
John Hallihan
Michael Halloran & Susan MacEachron
David Hamilton & Adam DiPaolo
Jennifer Hand & Tom Tierney
Jean Hansell
Fred & Shirley Harbold
Ruth Harlow & Diedre Sullivan
Adelaide & Bill Harris
Susan Hassler
Pete Hathaway
Rebecca Hathaway
Sally Haver & Bob Ellwood
Leila Hawken
Jack & Kathleen Hawley
Aloysius & Marguerite Hayes
Louis & Elaine Hecht
David Heck
Inge Heckel
John & Ann Hedbavny
Berel & Claire Held
Ann Coleen Hellerman
Nancy Hengen
Anne Hepner
Kathleen Herald & Michael Marlowe
Dick Hermans & Priscilla Herdman
Mary Herms & Ryan Marshall
Caroline Herrick & Ted Sands
Ed Herrington & Janis Cronk
Jon & Rindy Higgins
Chris Hiland
Kate Hinkle
John Hoffman
Neal Hoffman
Eric & Janet Honick
Maria Horn
Beverly House
Frederic Howard
Daniel & Dorcas Hubbard
David & Anne Hubbard
Sandra Huckleberry
Frank & Linda Hufner
Gary Hufner
George Huften
Nancy & Neil Humphreys
DeeAnne Hunstein
Diego Ibarguen & Laura Rigolosi-Ibarguen
Blanche & Nicholas Isabella
Beth & Jack Isler
Michael Jacoff
Gerald Jamin & Claudia Nalesnik
Pamela Jarvis
Patricia Jenny & Kent Hiteshew
Maureen Jerome
Elizabeth & Ian John
Johnnycake Books
John Jolly & Nicholas Pentecost
Jeanne Jones
Anita Jorgensen
Dan Kadlec
Carol & Richard Kalikow
Howard Kallstrom
Noah Kardos-Fein & Amy Scheim
Eugene & Marilyn Kay
Stephen & Belinda Kaye
Joel Kazis & Sara Nathan
Lynn Kearcher
Jeffrey & Claudia Keenan
Charles & Angeliki Keil
Robert & Jane Keiter
Peter & Alice Kent
Richard & Galene Kessin
Robert Kessler & Nancy Prahofer
Sallie Ketcham
Stephen Ketterer & Ignacio Ramirez
David & Lisa Keyko
Kevin & Caitlin Kiley
Jeffrey Kimball & Pamela Hogan
William & Susan Kinsolving
Amy Klein
Tara & Russ Klein
Carol Kneeland
Betty Krasne
William Kronholm
Kenneth & Patricia Krushel
Rob Kuhbach & Sherrell Andrews
Marian & David Kuhn Beers
Harold Kuplesky
Sarah Laliberte
Richard Lambertson
John & Duff Lambros
Jonathan Landman & Bonnie Vangilder
John & Jaye Landon
Alexandra & John Lange
Richard & Mary Lanier
Kim LaReaux
Roxana Laughlin & Rebecca Hurlburt
Dwight Lee
Jamie Lehrer & John O’Brien
Kate Lehrer
Lucy Lehrer & Richard Mack
Lois Lenehan & Burt Hanback
Peter Lese
Patricia Leshane
Michael Levengood
Macey Levin & Gloria Miller
Joan & James Levine
Joan Lewis & Vickie Tillman
Roger & Florence Liddell
Kenneth & Irene Liegner
Louise Lindenmeyer & Eliot Osborn
Lee & Fritz Link
William & Virginia Littauer
William Little, Jr. & Helen Yee Little
Michael Lonergan
James & Pamela Longwell
Alex Lotocki & Susan Sigda
Low Road Foundation
Jodi Luby
Joann Luning
Brenda Wehle & John Lynch
Rosemary Lyons-Chase
MacArthur Foundation
Anne MacDonald
Caitlin Macy & Jeremy Barnum
Carol Magowan
Julie Mallin
Georgette & Charles Mallory
Barbara Maltby
David Maltby & Chelsea Altman
Sarah Maltby & Louis Petrillo
Janet Manko
Gavin Marr
Rita Marshall
Peggy & Oscar Martinez
George Massey
Blaine & Deanna Matthews
Carolyn & Robert Mattoon
Edwin Maynard
Douglas McArthur
Cameron & Robin McClearn
Alan & Priscilla McCord
Joan McCue
Stephen & Katherine McCurdy
Dale McDonald
Camilla & Hugh McFadden
Judith & Raymond McGuire
Jean & Foster McMillen
Gerald McNamara Jr. & Renee Petrofes
Robert McSween
Robert & Althea Meade
Miami Foundation
Laura & Edward Midgley
Benjamin & Jan Miller
Lynden Miller
Dennis Mincieli & Debra Allee
Elizabeth Mitchell
Thordis Moeller
Carrick Mollenkamp
Barbara Kahn Moller & Karsten Moller
Margaret Monaco
John & Hope Mongeau
William Montgomery
David & Debbie Moore
Leslie & Nick Moore
Sheila Moore
Jeff & Molly Morgan
Kelly Morgan
Susan & Robert Morgenthau
William & Mary Sue Morrill
Scott Morris & Elyse Harney Morris
Elizabeth Morrison
Sarah & Tom Morrison
Eric Morrow
George & Istar Mudge
Andrew Murphy
Diane Murphy
Albert Muzaurieta & Annie Bell Muzaurieta
Suzanne Myers & Adam Pincus
Michael & Irene Nachwalter
Donald Najdek
Phyllis Nauts
Loek Neimeth
Michael Nesbitt
Karen Nickerson
Carolyn Noble
Mehrdad & Merilee Noorani
Robert Norman & Dee Salomon
North East Ford
Geraldine O’Neill
Thea & David Obstler
David & Janet Offensend
Suzanne & Peter Oliver
Roberta Olsen
Philip Oppenheimer & Mary Close Oppenheimer
Michelle Ores
Joan Osofsky
Richard & Jean Osofsky
Sanford Padwe & Daphne Hurford
Paley’s Farm Market
Elizabeth Park
Thomas Parrett
Sapna Parwani
Anne & Darryl Peck
Nina Peek
Paula Pelosi
Edward & Carol Peltier
Cheryl & Don Perdue
Jennifer Perga & Michael DeClement
Francis & Dolores Perotti
Ann Perse
Alexandra & Frederick Peters
Barbara Peterson
Elise Pettus
Lizbeth Piel
Barry Pinchoff & Barbara Zucker-Pinchoff
Susan Pinsky & Marc Rosen
Harry & Karen Pinson
Robert Pittenger & Carol Ascher
Plantin Seeds, Inc
Camilla and Oliver Platt
Kathy & Andrew Plesser
John Pogue
Leonard Polletta
Nicholas & Lee Potter
Christopher Pouler & Elizabeth Slotnick
Richard Primoff
M. Purnell
Alice Quinn & Laurie Kerr
Thomas Ragan
Carol & Larry Rand
Curtis & Susan Rand
Rosina Rand
Clare Rashkoff
Jeremy Rassen
Robert & Deborah Rathbun
Bernard Re, Jr.
Elliott Rebhun & Brad Voigt
Joan Redmond & Susan Crossley
Tamara Earles
Beverly Reich
Richard & Lynn Reifsnyder
Allen Reiser & Nora Jordan
Peter & Susan Restler
John Rhodes & Lucy Allen
Peggy Rice
David & Cristin Rich
Anne Richardson
William Riiska
Lisa Riley
Louise Riley
Sandy & Dick Rippe
Rachel & Richard Robbins
Eric Roberts & Robbianne Mackin
Leda Roberts
Mary Robertson
Roxana & Tony Robinson
John Robshaw
Dana & Fritz Rohn
Conley & Meredith Rollins
Brian & Lucinda Ross
Colin Ross
Dennis & Victoria Ross
Helen Ross
Peter & Michelle Roth
Susan Rothschild & Don Freedman
Amy Rothstein
Edward Rothstein
Patricia & Guy Rovezzi
Patricia Rowell & Ron Becker
Jeffrey & Susan Rubenstein
Catherine Ruggieri
Maureen Rule
Dan Russell & Mary Carroll
Carol Sadlon
Arlene & David Sampson
Philip & Marian Santoli
Ann Sartori
Kenneth & Edith Schechter
Eric Schnall & Shax Riegler
Harvey Schussler
Rhonda Schwartz & Stephen Wermiel
Pamela Scott & Phil Balshi
Teresa Scott
Cathryn & Thomas Scoville
Joseph & Carol Seaman
Janine Selendy
Tom Shachtman & Harriet Shelare
Lisa Sheble
Charles Short
Marvin Shulsky
Catherine Shyer
Scott Siegler & Claudia Gersh
Silver Mountain Foundation for the Arts
David Singer
Julie & Dag Skattum
David & Ruth Skovron
Isabel Sloane
Laurie Slotnick
Betsy Smith & Rick Cotton
Ileene Smith & Howard Sobel
Marge Smith
Peter & Agneta Smith
Sandy Smith
Amy Smith-Hull
Emily Soell
Natalie Solan
Kathleen Spahn
William Spalding
James Speyer & Audrey Lavin
John & Elizabeth Sprague
Mona Staaf-Gunther
David & Sarah Stack
Richard Stalzer
Kurt Stampfle & Linda Patz
Benjamin Stapleton
Emily & Steven Steinman
James Stengel & Beverly Jean Bartow
James Sterba
Kate Stiassni & Ned Nunes
Addison Stone
Rachel & Donald Strauber
John Striker
Liz and Maurice Stucke
Mary Sullivan
John Sutter & Kathleen Kucka
Virginia Suttman
Andrew & Louise Swanson
Jessica Swartz & Asa Davis
Kelly Sweet
Joanne Taber
Joan Taylor
Mary Taylor
Peter & Anna Tcherepnine
Sarah & Richard Tennyson
Maureen Tesoro
The deBart Group
Douglas Thomas
Craig Thompson
Anna Timell
Clare Timoney & Joseph Kelly
James Traub
Tow Foundation
Tom & Nancy Trowbridge
William Trowbridge
Heidi Truax
Nora Tulchin
Jonathan Tunick & Leigh Beery
Rusty Tunnard
Scott & Pamela Ulm
Gary & Elizabeth Unger
Dawn Upshaw
Rise & Quentin Van Doosselaere
Kristen van Ginhoven
Peter Vaughn & Hiram Williams
Sally Vaun
Eric Veden
John Virden III
Amy Virshup
Kathleen & Michael Voldstad
Betsy Vorce
Karen Vrotsos & David Rogers
Cynthia Walsh & Rene Milo
Larry Walsh & Gael Doar
Nancy Ward
Claudia Warner
Gordon Warnke & Laurie Batchelor
Arete Warren
Tom Watson
Jeanette Weber
Hedwig Wells
Lyn Westsmith
James & Karin Wexler
George Warren Whitaker
Thomas Whitridge
Leah Wilcox
Austin & Martha Wilkie
Bunny Williams & John Rosselli
Bill & Roberta Willis
Adolph & Barbara Wismar
Frank & Lisa Wohl
Howard Wolfson
Susannah & Willard Wood
Lillian Woodworth
Catherine & Edward Woolston
Timothy Wright & Abigail Nova
Amy Wynn
Alice Yoakum
Grace Yowell
Linda Yowell & Richard Zuckerman
Jared Zelman & Pamela Chassin
Murray & Martha R. Zimiles
Barbara & Michael Zimmerman
*The Lakeville Journal and The Millerton News operate as a 501(c)(3) organization and gratefully acknowledge our donors who help us achieve our mission. The listing above includes donors who have given to LJMN between January 1, 2025 and January 31, 2026.
We have attempted to make this list as accurate as possible within the dates provided. If you are listed incorrectly,
or believe your name has been omitted, please accept our sincere apologies, and notify us at publisher@lakevillejournal.com.
Keep ReadingShow less
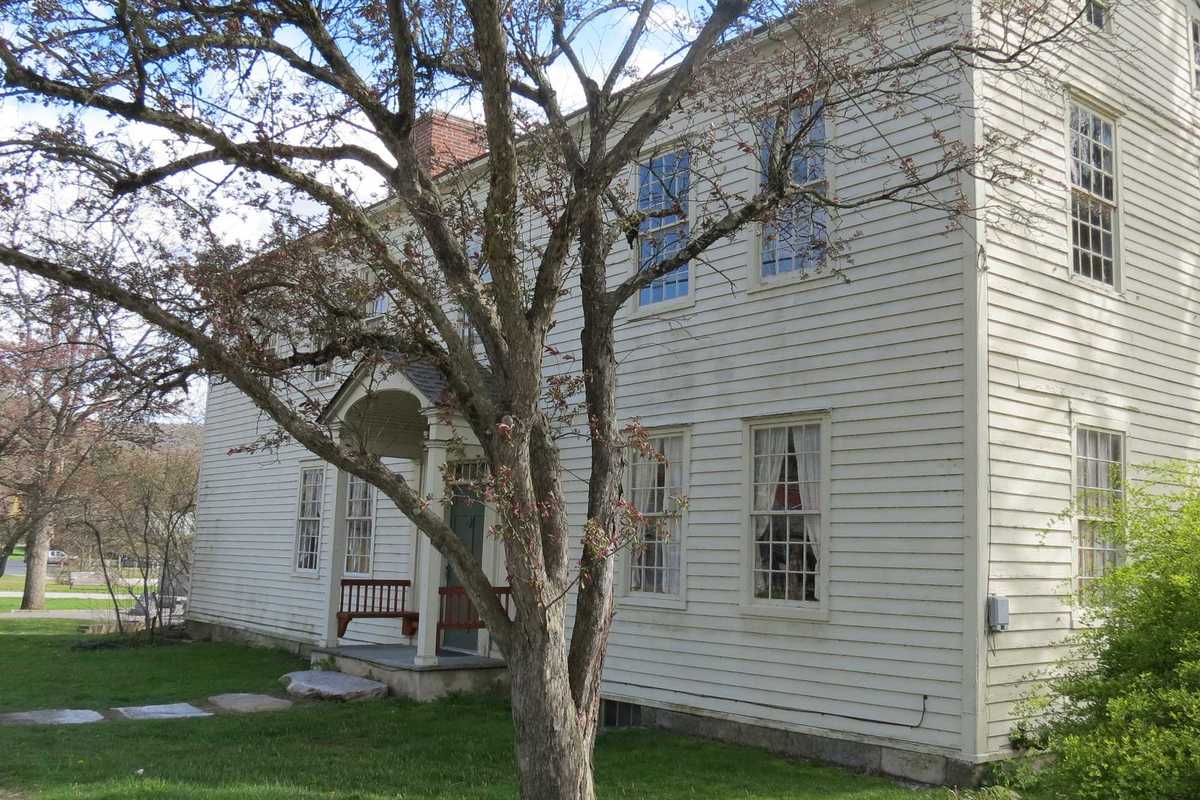
Swift House committee learns of potential buyer at first meeting
Ruth Epstein
Mar 01, 2026
Swift House in Kent.
By Ruth Epstein
KENT — The fate of the Swift House is once again front and center after the newly formed Swift House Investigation Committee held its first meeting Tuesday, Feb. 24 — and learned that a local attorney is interested in buying the historic property.
At the meeting’s outset, committee member Marge Smith said local attorney Anthony Palumbo has expressed interest in purchasing the building. “He loves it and said he’d be honored to buy it and maybe lease part of it back to the town. He would be OK with a conservation easement.” She said he supports several previously proposed uses, including a welcome center and exhibition space.
In response, Jason Wright, a committee member and representative of the town's Board of Finance, said he would favor “anything that keeps it off our financial statements. That sounds like a sweetheart deal that needs to be explored. An aspiration for me would be to see the house restored and be a gateway to the town.”
But committee chairman James Anderson urged caution. “I don’t think we should focus on one deal,” he said. “We have an obligation to do something with that space. We shouldn’t overrate this proposal. That’s a bad process in my mind.”
The historic building on Maple Street dates back to the mid-1700s and changed hands several times before being acquired by the town in the 1970s. Its first floor has been used over the years by civic organizations, including the Kent Historical Society and the Kent Informal Club. But with funding needed for upgrades and to make the building compliant with the Americans with Disabilities Act, questions have resurfaced about whether it should be retained or sold.
A Swift House Task Force was established several years ago. Members conducted a town survey and hired the firm Silver Petrocelli to draw up restoration plans, which were estimated to cost more than $2 million. The previous administration later disbanded the task force, leaving decisions about the house’s future to the current Board of Selectmen, which established the new committee.
Members are charged with providing input and assistance to the selectmen on a redesign, updated construction plans and ADA-compliant upgrades, as well as developing a secondary comprehensive plan to sell the building if the town decides to dispose of the property. The committee is authorized to represent the town but may not enter into contracts without approval. It was given a deadline of April 30 to present its findings.
The committee includes Selectman Lynn Harrington; Board of Finance representative Jason Wright; Marge Smith and Christine Adams of the Kent Historical Society; and James Anderson, William Reihl and Margie Austell. Anderson was named chairman.
Committee members also discussed possible uses, including a visitor center, meeting space for local organizations and exhibition space. Harrington said the group must identify uses the broader community supports if it expects to secure funding.
Adams, the newly appointed executive director of the historical society, said securing a conservation easement in perpetuity — and determining who would hold it — should be a top priority. She added that listing the building on the National Register of Historic Places could help attract visitors. Adams said a consultant she knows has successfully guided other organizations through the process, with fees ranging from $2,000 to $5,000.
Wright also suggested that the building’s possible connection to singer Taylor Swift could generate interest. Smith said the artist is a descendant of the brother of Jabez Swift, who built the original portion of the house. Wright said he knows members of Swift’s family and would attempt to make contact.
The committee will meet again on March 10 at 6 p.m. to discuss a potential easement, Palumbo’s interest, and any contact with the Swift family.
Keep ReadingShow less
Sharon median home price rises to $710,000 as inventory tightens
Christine Bates
Mar 01, 2026
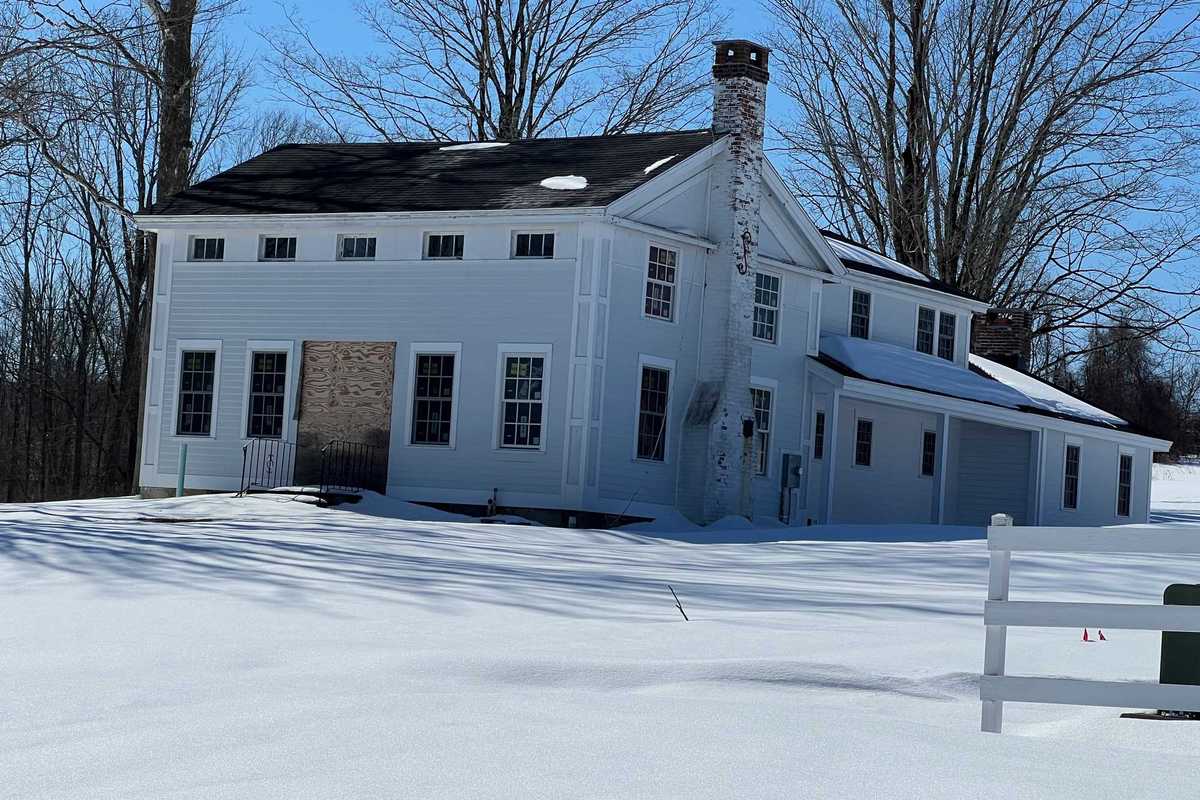
119 Amenia Union Road — A four-bedroom, 2.5-bath home built in 1872 on 4.42 acres recently sold for $522,500.
Photo by Christine Bates
SHARON — The 12-month trailing median price for a single-family home in Sharon increased to $710,000 for the period ending Jan. 31, 2026 — its highest point since September 2024 as home values across much of Connecticut continued to edge higher.
The figure marks an increase from the $560,000 median recorded for the 12 months ending Jan. 31, 2025, and from $645,000 for the comparable period ending Jan. 31, 2024. While January and February are typically slow months, the 12-month rolling figure reflects a broader reset.
The sales of single-family homes in Sharon on a 12-month rolling basis remained slightly below its historic range. A total of 38 single-family homes were sold in the 12 months ending Jan. 31, 2026, compared with 41 sales in the period ending Jan. 31, 2025, and 41 sales for the 12 months ending Jan. 31, 2024. Historically, annual sales of single-family homes in Sharon typically range between 40 and 50 transactions.
Inventory remains limited. At the end of February, there were 11 single-family homes on the market. Of those, nine were listed above $1 million and none were listed below the current $710,000 median price. Nine parcels of land are listed for sale on the MLS ranging from $139,000 to $585,000. Summer furnished rentals are now hitting the market for $8,000 to $25,000 a month.
Transactions
15 Herrick Road - 3 bedroom/2.5 bath home on 2.32 acres sold by Jesus Desantiago and Carol Haug to David and Mary Kathleen Fowler for $2,100,000.
96 Knibloe Hill Road – 2 bedroom/2 bath home on 2.05 acres sold by Marcel and Claudia Antonietta Vittoria Saucy to Ruth Godbout for $710,000.
10 Surdan Mountain Road – 3 bedroom/2 bath ranch on 2.09 acres sold by Nicholas Louis Terzo to Peter Scott Navario and Travis Blakeslee Jones for $615,000.
287 Amenia Union Road – 3 bedroom/1.5 bath cottage built in 1800 sold by Thomas Casey Sunderland and Charlotte Cohen Sunderland to Aiden Bowman and Joshua Metersky for $703,500.
9 Holland Drive -3 bedroom/1.5 bath Cape on 3.05 acres sold by Arthur Hagendorf to Michael and Patricia Collins for $375,000.
119 & 121 Amenia Union Road – 4 bedroom/2.5 bath house built in 1872 on 4.42 acres and 2 bedroom/1.5 bath barn on 4.42 acres sold by 32 Railroad LLC to CJMD 2 LLC for $522,500 for each property.
* Town of Sharon real estate transfers recorded between January 1, 2026, and January 31, 2026, provided by Sharon Town Clerk. Transfers without consideration are not included. Current market listings from Smart MLS. Note that recorded transfers frequently lag sales by a number of days. Compiled by Christine Bates, Real Estate Salesperson with William Pitt Sotheby’s International Realty, Licensed in CT and NY.
Keep ReadingShow less

Want more of our stories on Google? Click here to make us a Preferred Source.
Kent's towering snowman honors Robbie Kennedy
Ruth Epstein
Feb 28, 2026
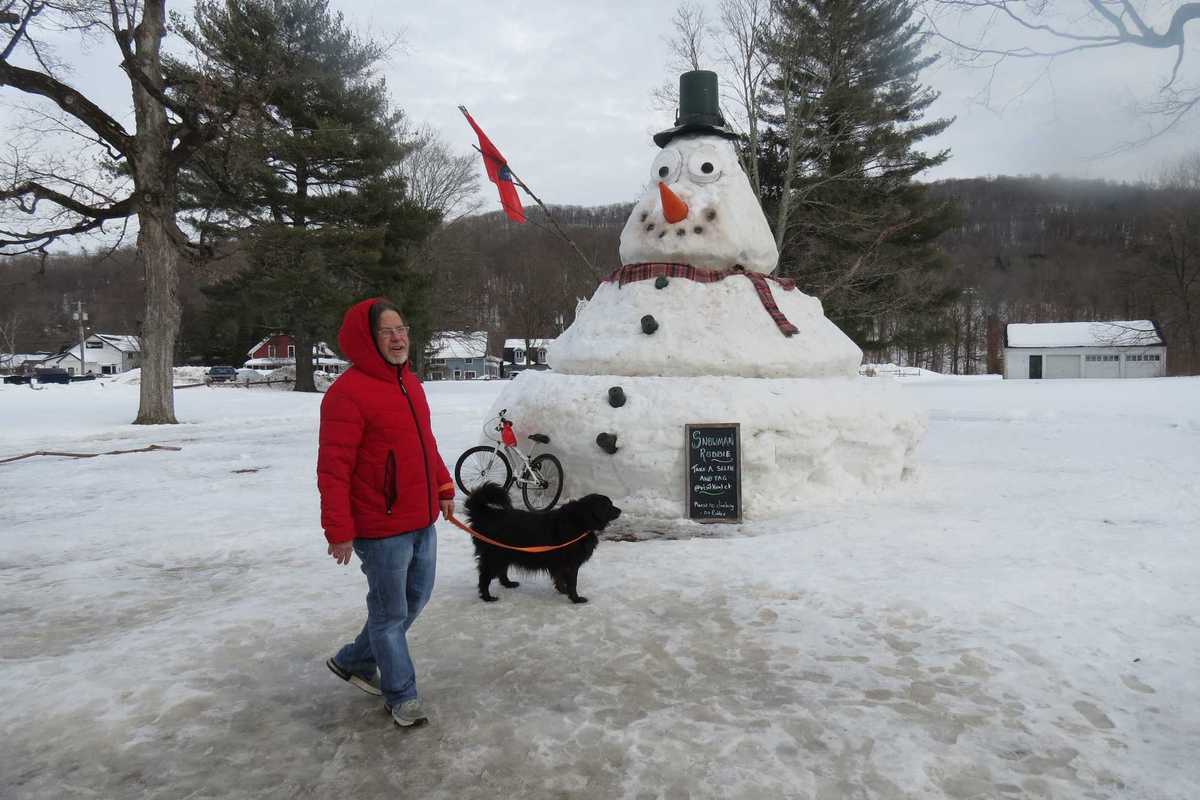
Jeff Kennedy visits the 20-foot-high snowman located in the Golden Falcon lot in Kent that was created in honor of his late brother Robbie Kennedy.
Photo by Ruth Epstein
KENT – Snowman Robbie stands prominently in the center of town, just as its namesake — longtime Kent resident Robbie Kennedy — did for so many years.
The 20-foot-high frozen sculpture pays tribute to Kennedy, who died Feb. 9, at the age of 71. A beloved member of the community, he was a familiar sight riding his bicycle along town roads waving to all he passed. Many people knew him from his days working at Davis IGA, the local supermarket. He was embraced by the Kent Fire Department, where he was named an active emergency member and whose members chipped in to buy him a new bike, and by the Kent School football team where coach Ben Martin made him his assistant. At Templeton Farms senior apartments, he was the helpful tenant, always eager to assist his neighbors.
Last week Gary Kidd, Dan Greenbaum and Loghan Bennett decided to build a snowman on the Golden Falcon lot to honor Kennedy. The site was chosen because it is right across the street where his brother Jeff and family live and from where they operate their business, Foreign Cargo. Leaning against the creation is Kennedy’s bicycle. The snowman is holding flags that wave in the wind.
“Robbie was a cheerleader for the town, and we thought the flags were a way to show that,” Kidd said, who acknowledged that the trio didn’t start to make it that big, but it just grew.
“It’s dedicated to Robbie in the spirit of childlike enthusiasm at any age,” Greenbaum said on Facebook.
The creature, with its large eyes, plaid scarf and top hat, has become a great attraction in town. It was featured on a WFSB-TV segment, throngs of people have stopped to snap photos, and Kidd has talked to Kent Center School classes who have come out for field trips.
Among those who like to visit is Jeff Kennedy. “The outpouring for Robbie from townspeople has been amazing,” he said. “At one time there was talk of maybe having him move closer to other family members, but I said Robbie has to stay here. He belonged in Kent.”
Keep ReadingShow less
Classifieds - February 26, 2026
Lakeville Journal
Feb 25, 2026
Help Wanted
PART-TIME CARE-GIVER NEEDED: possibly LIVE-IN. Bright private STUDIO on 10 acres. Queen Bed, En-Suite Bathroom, Kitchenette & Garage. SHARON 407-620-7777.
The Salisbury Association’s Land Trust seeks part-time Land Steward: Responsibilities include monitoring easements and preserves, filing monitoring reports, documenting and reporting violations or encroachments, and recruiting and supervising volunteer monitors. The Steward will also execute preserve and trail stewardship according to Management Plans and manage contractor activity. Up to 10 hours per week, compensation commensurate with experience. Further details and requirements are available on request. To apply: Send cover letter, resume, and references to info@salisburyassociation.org. The Salisbury Association is an equal opportunity employer.
Gardeners needed for native plant design business: March 15-December 1st. Must be physically fit and dependable. Call for interview 347-496-5168. Resume and references needed.
Weatogue Stables in Salisbury, CT: has an opening for experienced barn help for Mondays and Tuesdays. More hours available if desired. Reliable and experienced please! All daily aspects of farm care- feeding, grooming, turnout/in, stall/barn/pasture cleaning. Possible housing available for a full-time applicant. Lovely facility, great staff and horses! Contact Bobbi at 860-307-8531. Text best for prompt reply.
Services Offered
Hector Pacay Landscaping and Construction LLC: Fully insured. Renovation, decking, painting; interior exterior, mowing lawn, garden, stone wall, patio, tree work, clean gutters, mowing fields. 845-636-3212.
PROFESSIONAL HOUSEKEEPING & HOUSE SITTING: Experienced, dependable, and respectful of your home. Excellent references. Reasonable prices. Flexible scheduling available. Residential/ commercial. Call/Text: 860-318-5385. Ana Mazo.
Pets

12 week old black and tan/blue tick coonhound: mix for sale. First set of puppy shots done at 8 weeks. Call 860-248-9947 for more info. and price.
Real Estate
PUBLISHER’S NOTICE: Equal Housing Opportunity. All real estate advertised in this newspaper is subject to the Federal Fair Housing Act of 1966 revised March 12, 1989 which makes it illegal to advertise any preference, limitation, or discrimination based on race, color religion, sex, handicap or familial status or national origin or intention to make any such preference, limitation or discrimination. All residential property advertised in the State of Connecticut General Statutes 46a-64c which prohibit the making, printing or publishing or causing to be made, printed or published any notice, statement or advertisement with respect to the sale or:rental of a dwelling that indicates any preference, limitation or discrimination based on race, creed, color, national origin, ancestry, sex, marital status, age, lawful source of income, familial status, physical or mental disability or an intention to make any such preference, limitation or discrimination.
Real Estate For Sale
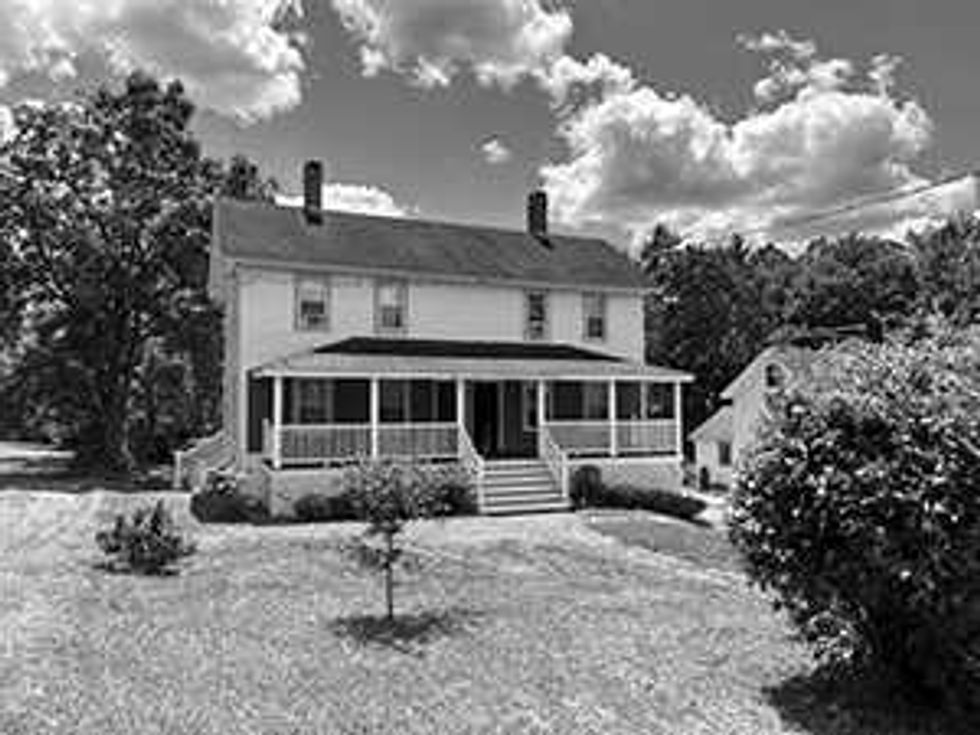

FOR SALE: 39 Hospital Hill Road, Sharon. 1680 sq.ft. Two family, rare side-by-side units. 4 bed; 2 full bath, 2 half. Great investment, or live in one and rent other side. $485,000. Call/text Sava, 914 -227-4127.
Business Opportunities
FOR RENT COMMERCIAL KITCHEN IN FALLS VILLAGE: Located in the heart of Falls Village. 425 sf space fully equipped for catering business, wholesale food prep or bakery. Several successful local businesses got their start here! Event space in building could be available. Contact anita@100mainst.com.
Keep ReadingShow less
To save birds, plant for caterpillars
Dee Salomon
Feb 25, 2026
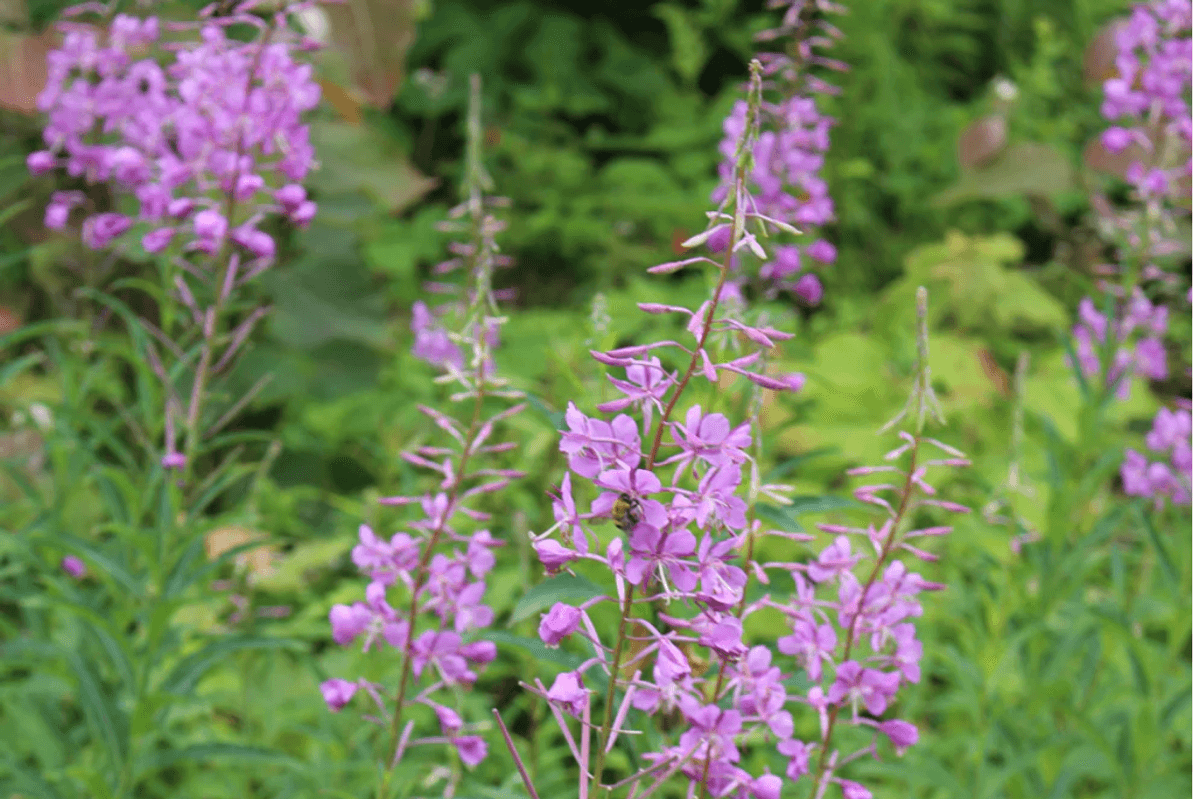
Fireweed attracts the fabulous hummingbird sphinx moth.
Photo provided by Wild Seed Project
You must figure that, as rough as the cold weather has been for us, it’s worse for wildlife. Here, by the banks of the Housatonic, flocks of dark-eyed juncos, song sparrows, tufted titmice and black-capped chickadees have taken up residence in the boxwood — presumably because of its proximity to the breakfast bar. I no longer have a bird feeder after bears destroyed two versions and simply throw chili-flavored birdseed onto the snow twice a day. The tiny creatures from the boxwood are joined by blue jays, cardinals and a solitary flicker.
These birds will soon enough be nesting, and their babies will require a nonstop diet of caterpillars. This source of soft-bodied protein makes up more than 90 percent of native bird chicks’ diets, with each clutch consuming between 6,000 and 9,000 caterpillars before they fledge. That means we need a lot of caterpillars if we want our bird population to survive.
So how do we ensure that there are sufficient caterpillars for them? That is the question, as caterpillars are very particular. Their butterfly or moth mothers cleverly attach their eggs to the very specific plants their tiny babies require. Once they hatch, the caterpillars eat the leaves of these plants until they are either picked off by birds to feed their young or create a chrysalis and turn into a moth or butterfly to repeat the cycle of life.
Some caterpillars are generalists and can survive on a variety of plants, but most — 90 percent, according to scientists — are specialists, relying on only one or two types of plants for survival. In their winged form, dietary restrictions ease as they source pollen more widely, but when it comes time to lay eggs, they use a keen sense of smell to find the specific plants that will help their young survive.
Research by Doug Tallamy shows that 90 percent of butterfly and moth species rely on just 14 percent of native plant species for food, which makes the planting of these “keystone” plants critical. Let’s review a few.
Goldenrod: Not all goldenrod is created equal. Old field goldenrod, (Solidago nemoralis), is a shorter and less aggressive alternative to the tall, aggressive goldenrod we are familiar with, as is wrinkleleaf goldenrod, (Solidago rugosa), a compact species that has arching sprays of bright yellow flowers supporting more than 100 species of insects. This species is deer-resistant with no serious pests or diseases. Last year, Mt. Cuba Center, a conservation center out of Delaware, focused its trials on goldenrod, and its research report, available online, is sortable not just by aesthetic attributes but also by the number of insects seen on each species.
Scarlet strawberry: (Fragaria virginiana), is one of the plants I have had great luck growing in the woodland. When there is a new sunny spot, which happens when a tree or large branch falls, I plant a few strawberries, which I dig out of a spot where they are thriving. These plants make a great groundcover and are especially nice used under trees for caterpillar “soft landings.”
Spotted Joe-Pye weed: We see this plant, (Eutrochium maculatum), on roadsides in late summer, but it looks as sharp as an ornamental in the hands of Michael Trapp, who, in the garden behind his shop in West Cornwall, encloses a bed of Joe-Pye weed with a short boxwood hedge, dignifying this plant that supports between 35 to 40 caterpillar species, including those that become the three-lined flower moth, Clymene moth, ruby tiger moth, Eupatorium borer moth and great spangled fritillary moth.
I am less familiar with fireweed, (Chamaenerion angustifolium), but will be adding it this year, as it may be the prettiest of the keystone plants in our region and attracts the fabulous hummingbird sphinx moth. I will let you know when I find a local nursery that stocks it and, when planted, how it fares here.
Also keep in mind this spring: smooth aster, (Symphyotrichum laeve); white yarrow, (Achillea millefolium); and the beautiful Canadian columbine, (Aquilegia canadensis), which is the first food for hummingbirds’ arrival in the Northwest Corner.
Dee Salomon ‘ungardens’ in Litchfield County.
Keep ReadingShow less

Want more of our stories on Google? Click here to make us a Preferred Source.
loading