Latest News
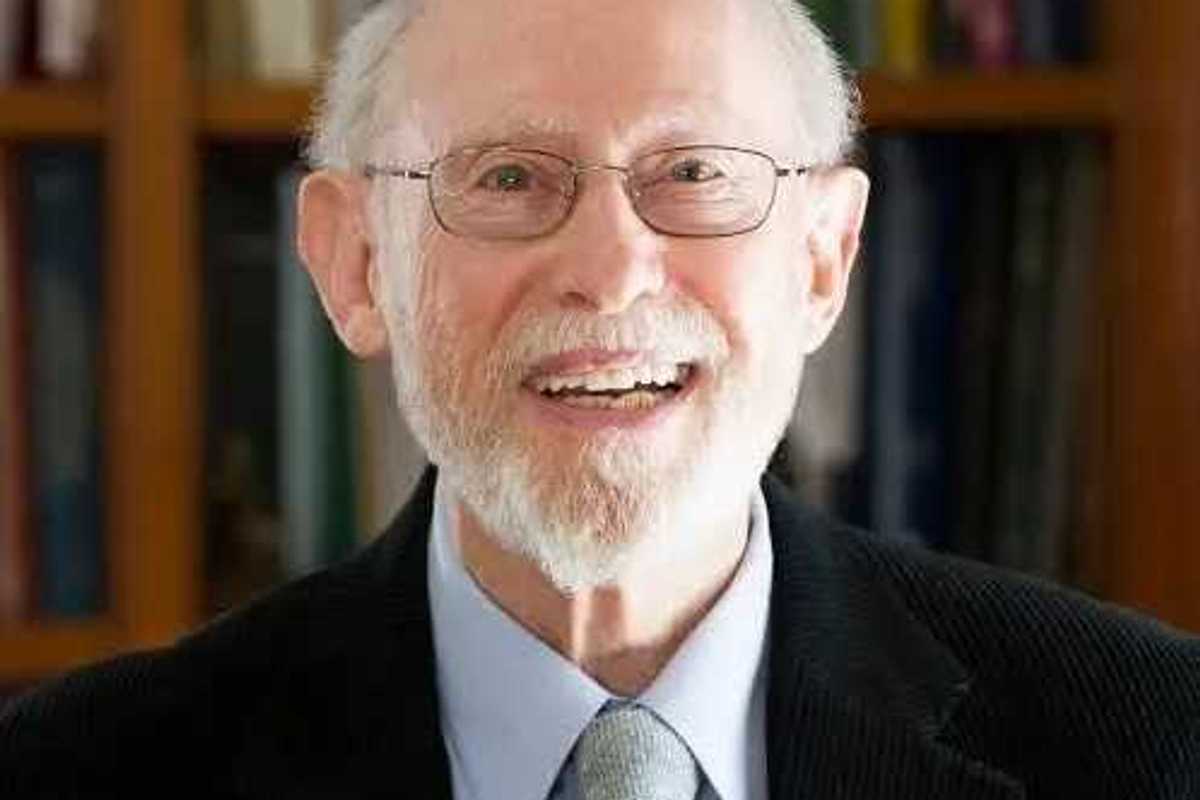
Alfred Lyon Ivry
Lakeville Journal
Mar 11, 2026
SALISBURY — Alfred Lyon Ivry, a long-time resident of Salisbury, and son of Belle (Malamud) and Morris Ivry, died in Bergen County, New Jersey, on Feb. 12 at the age of 91, surrounded by family members. Born and raised in Brooklyn, he was a graduate ofAbraham Lincoln High School and Brooklyn College, where he earned a B.A. in English literature and Philosophy and served as drama critic for the school paper.
Alfred earned a PhD in Medieval Jewish Philosophy from Brandeis University in Waltham, Massachusetts in 1963 and in 1971 was awarded a D. Phil in Medieval Islamic Philosophy from Oxford University, Linacre College.
He enjoyed a long career as a professor of Jewish and Islamic philosophy, with appointments at Cornell, Ohio State, Brandeis, and New York University. Alfred wrote more than one hundred scholarly articles and book reviews, and was the author or editor of nine books, including Maimonides’ Guide of the Perplexed: A Philosophical Guide, published in 2016.
Alfred and Joann, his wife of 67 years, moved to the Berkshire area in the early 1990s, splitting their time between the Twin Lakes and New York City until their respective retirements. After that, they lived in Salisbury full time, availing themselves of the region’s many cultural offerings. They relocated in late 2020 to Noble Horizons for two years before moving to New Jersey to be closer to their children.
In their many years together, Alfred and Joann traveled regularly, frequenting museums, national parks, and other destinations. Alfred was an avid reader of the newspaper, fiction, and poetry, and possessed both a sharp wit and an estimable sense of humor. Throughout his life, he enjoyed outdoor activities including swimming, camping, hiking, ice skating on Twin Lakes, and tennis. Like many Brooklyn boys of his era, he followed the Dodgers, but happily took his children to Red Sox games at Fenway Park and later his grandchildren to see the Red Sox at Yankee Stadium.
In Salisbury, Alfred became a successful gentleman farmer, and embarked on canoe trips and fishing expeditions on Twin Lakes and beyond.He took up birding, among other hobbies, and with Joann developed and enjoyed the friendships he made in Salisbury and environs, and especially amongst members of the Great Barrington-based Berkshire Minyan, of which they were founding members.
Above all, Alfred was committed to the Jewish tradition and people, and to his family. He is survived by his wife, Joann (nee Saltzman);children, Rebecca and husband Clifford Stein, Jonathan, Sara, and Jessica, grandchildren; Molly and husband Josh Mark, Noah and wife Noa Shapiro, Ben Stein, Talia, Max, Isaiah, and Esther Ivry; great-grandchild, Aaron Mark; and colleagues and friends made throughout his life. He was predeceased by his sister, Grace.
Donations in Alfred’s memory may be made to the Berkshire Minyan and to the Yaakov Goboff Fund at the Yaakov Herzog Institute for Jewish Studies.
Keep ReadingShow less
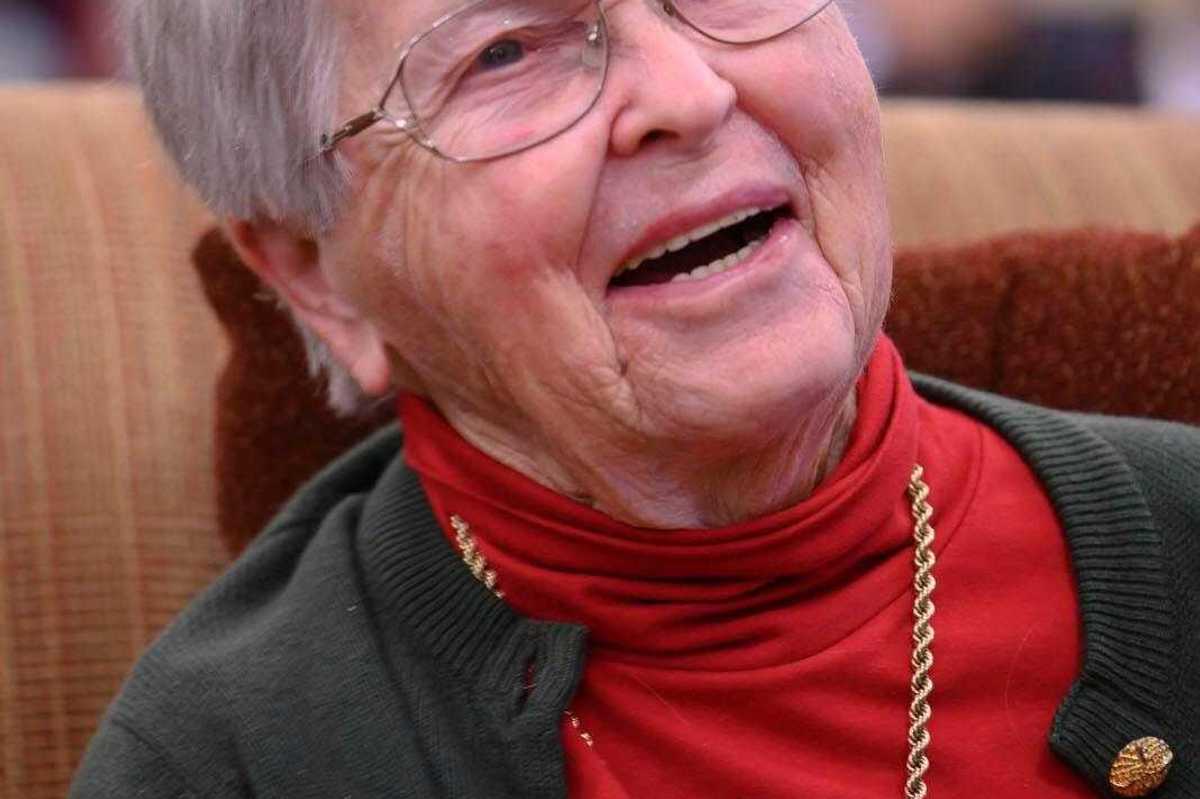
Alice Gustafson
Lakeville Journal
Mar 11, 2026
LAKEVILLE — Alice Gustafson (née Luchs), 106, of Lakeville, Connecticut, passed away on March 2, 2026. Born in Chicago on Dec. 15, 1919, Alice was raised between New York City, Florida and Lime Rock, where she graduated from Salisbury High School in 1937.
Alice’s career spanned roles at Conover-Mast Publications in New York City, The Lakeville Journal, the Interlaken Inn, and as a secretary to the past president of Smith College. In 1948, she married Herbert “Captain Gus” Gustafson at Trinity Church in Lime Rock.
A devoted community servant, Alice volunteered for twenty years at White Plains Hospital and for over thirty years at Sharon Hospital. She was a passionate supporter of the arts, notably through her involvement with Music Mountain and Crescendo Music Program. She was also an active member of the Salisbury Congregational Church, the Nichi Bei Fujinkai society, and served as a docent at Philipsburg Manor.
Alice is survived by her son, Gordon Gustafson, and his wife Christine, her daughter Elizabeth (DeeDee) Dohan, and her husband Andrew, her grandchildren and great grandchildren. She was preceded in death by her husband, Herbert.
Her celebration of life will take place on Saturday, June 6, at 11:00 a.m. at the Congregational Church of Salisbury.
While flowers are a lovely tribute, those who wish to further honor Alice’s memory may consider a contribution to Music Mountain, Crescendo, or the Congregational Church of Salisbury.
Keep ReadingShow less
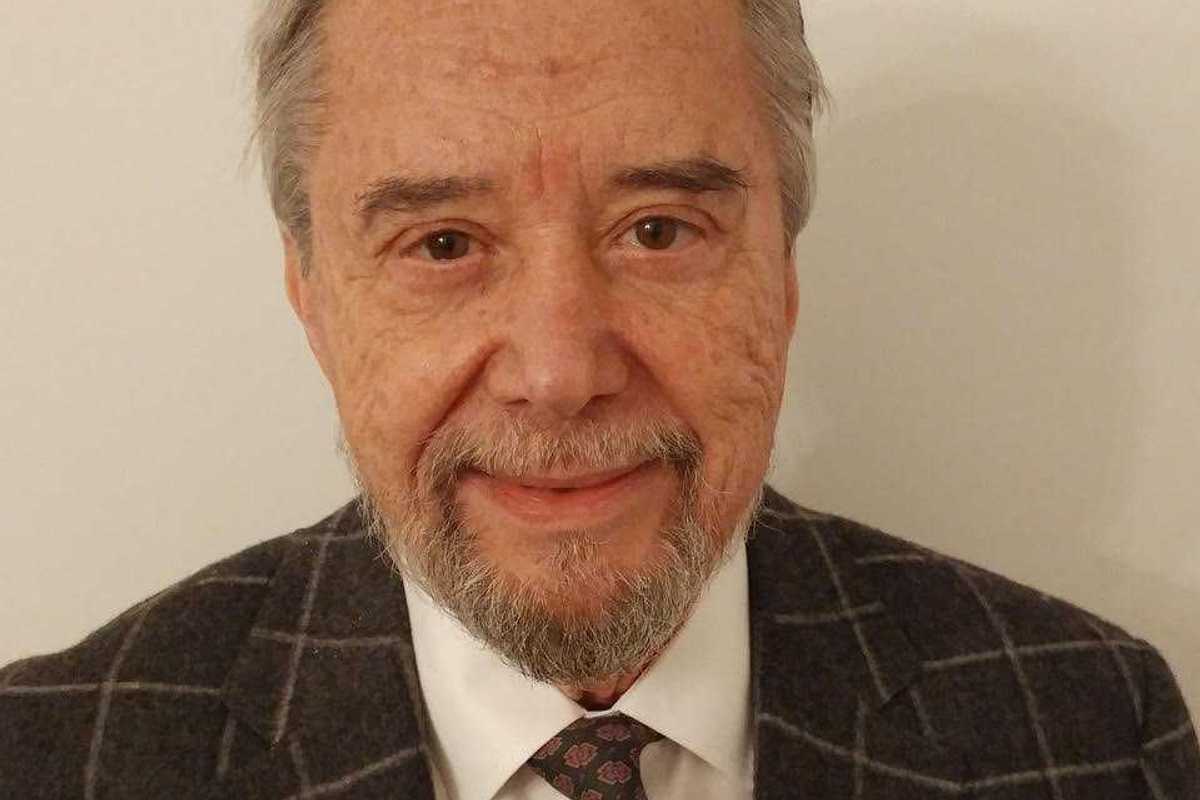
Larry Power
Lakeville Journal
Mar 11, 2026
LAKEVILLE — Larry Power passed away peacefully at home on March 9, 2026.
Larry was born at St. Vincent’s Hospital in New York City in 1939.
He had a successful public relations firm for over 35 years in NYC.
After retiring, he chaired the Sharon Land Trust board for many years. He always said one of the most important things he ever did was saving the Twin Oaks Field from development.
He is survived by his husband Lea Davies of 44 years.
Donations in his memory can be sent to East Mountain House in Lakeville in honor of Keavy Bedell or the Sharon Hospital Primary Care Project in honor of Doctor Jonathan Joseph.
The Kenny Funeral Home has care of arrangements.
Keep ReadingShow less

Want more of our stories on Google? Click here to make us a Preferred Source.
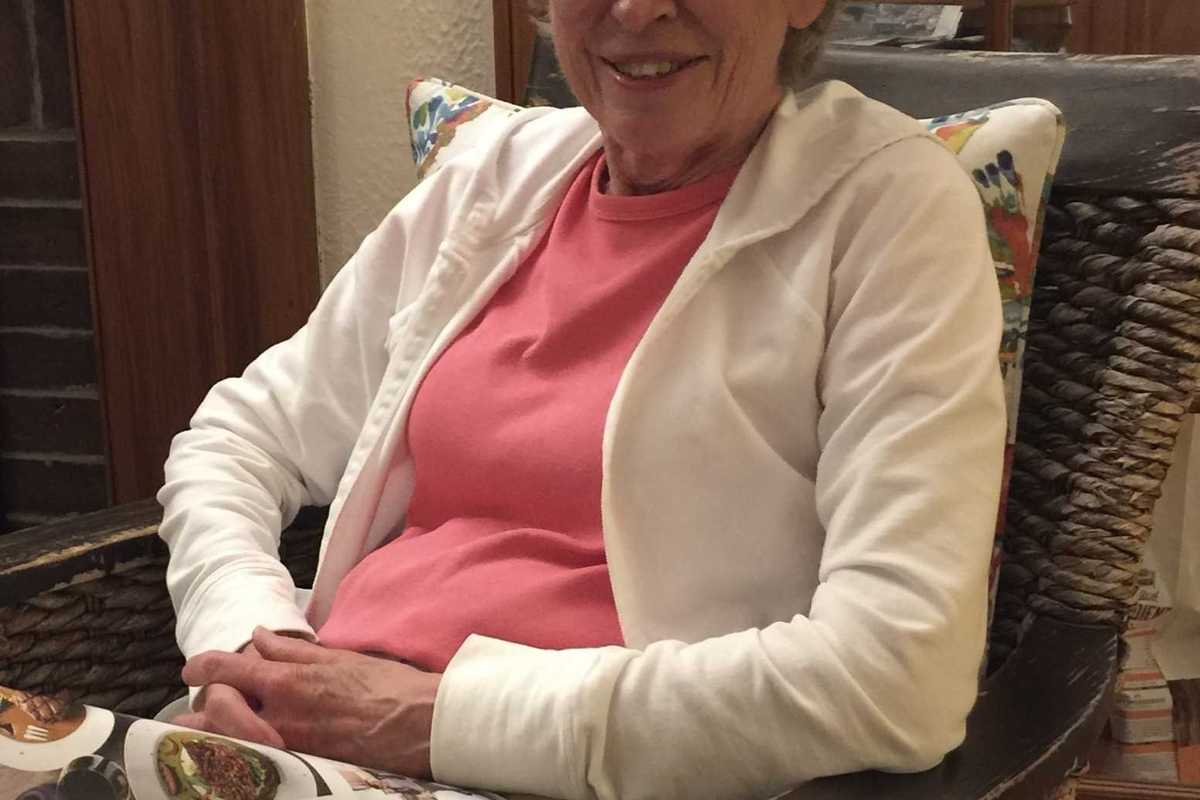
Carol Hoffman Matzke
Lakeville Journal
Mar 11, 2026
KENT — Carol L. Hoffman Matzke passed away peacefully with family by her side on Feb. 22, 2026.
She was a beloved mother and stepmother, daughter, sister, grandmother, great-grandmother, community member, and friend.Her presence will be deeply missed. She had a beautiful way of loving, accepting, and supporting all the many members of her vast family, and of welcoming others into her family circle. She was intelligent and well-informed about history and current events, and she took a genuine interest in knowing and understanding everyone she met, from friends and family right down to the stranger who stood next to her in line at the grocery store. Kind and generous, her family and friends knew that she would do anything in her power to help and support them.
Carol was the oldest of five children, born on June 21, 1939 in Springfield, Vermont to Janet (Beal) Lawrence and John Lawrence. She graduated from Mt. Lebanon High School in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania in 1957. She attended Colby College, graduating with a history degree in 1961. She was married and widowed twice, first to John Hardie Hoffman (1935-1984) and second to William A Matzke, Jr. (1924-2001).
In 1976 she and her husband, John, moved to Kent, to realize their dream of opening a small retail bookstore which they named The House of Books. Carol and John blended seamlessly into the community, and The House of Books quickly became part of the fabric of Kent where it has continued to welcome and serve the readers and writers of the area.
Carol was an active member of St. Andrews Episcopal church, where she served in various roles throughout the years. She was also an avid tennis player throughout her life and could often be found in the midst of a competitive match on the Kent School courts.
In 1993, Carol shifted her full-time residence to Seattle, Washington where her eldest daughter, Cathy resided with her family.It was in Seattle that she met and married her second husband, William A Matzke, Jr. Carol and Bill had a vibrant life in the Seattle area where she supported her children and step-children in raising their families, volunteered for The Fisk Genealogical Library, the USO at Sea-Tac Airport, and was an active member of two church communities: Evergreen Covenant Church in Mercer Island, Washington and St Mark’s Cathedral in Seattle, where she served as senior warden.
In 2017, after many years splitting her time between Seattle and Kent, Carol settled full-time in Kent. Carol was frequently spotted walking her dog along Kent’s roadways, sometimes in the pre-dawn darkness. She was a regular at the soccer games, plays, concerts, and other activities of her many New England grandchildren.
In 2024, Carol found a loving home with her daughter Barb’s family in Upton, Massachusetts, eventually transitioning to memory care at Keystone Place in Torrington, where she passed peacefully with loving family and caregivers by her side.
Carol is survived by her daughters, Cathy Miller, Barbara (and David) Lundbom and Tracy (and Rich) Horosky; stepson Scott Hoffman; stepdaughters Lori (and Dick) Ehrig, Andrea Matzke, Cynthia Matzke, and Lisa Matzke as well as 15 grandchildren and 7 great grandchildren. She is also survived by her siblings, Johanne LaGrange, Rod (and Fayne) Lawrence and Ann Wessel. She was pre-deceased by husband John Hardie Hoffman (1984), husband William A. Matzke, Jr. (2001), stepson John Morris “Jay” Hoffman (2023) and sister Gale Lawrence (2024).
Memorial services are planned in both Kent and Seattle later in the spring.Remembrances honoring Carol’s life can be made to the Kent Library Association (P.O. Box 127, Kent, CT 06757) or the Northwest USO (17801 International Blvd, PMB #313, Seattle, WA 98158).
Keep ReadingShow less
In remembrance: Grace E. Golden
Lakeville Journal
Mar 11, 2026
Cornwall signs contract for new fire trucks
Riley Klein
Mar 11, 2026
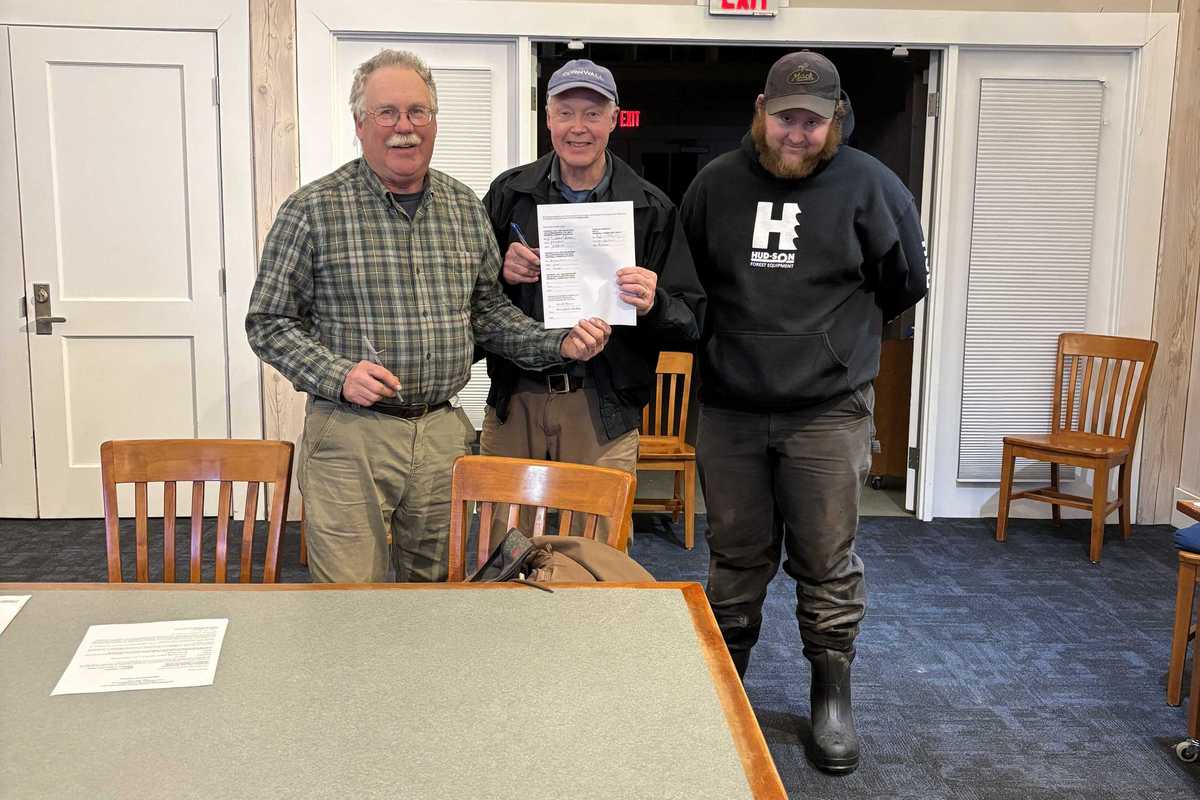
From left, is First Selectman Gordon Ridgway, Dick Sears and CVFD Chief Will Russ signed the contract for two new fire trucks March 3.
Provided
CORNWALL — Cornwall Volunteer Fire Department and the Board of Selectmen signed the contract for two new fire trucks Tuesday, March 3.
The custom rescue pumper and mini pumper will be manufactured by Greenwood Emergency Vehicles, located in North Attleboro, Massachusetts.
The cost is $1.2 million and the estimated delivery time is mid-2027. CVFD raised $600,000 in donations, which will be paired with money from the town’s truck fund.
Greenwood had the lowest price and fastest delivery time of the three manufacturers that submitted bids.
The new vehicles will replace outdated trucks that are both more than 25 years old.
Keep ReadingShow less

Want more of our stories on Google? Click here to make us a Preferred Source.
loading