After two fraught weeks in Dubai, where government ministers from around the world haggled over how to confront climate change, the U.N. conference COP28 closed on Dec. 13 with a deal that calls on countries to move away from fossil fuels — the oil, gas and coal fueling the climate crisis — by 2050 and to triple the capacity for renewable energy by 2030.
While the U.N. hailed the agreement as the beginning of the end of the fossil-fuel era, skeptics, critics, cynics and climate scientists were less impressed. They had hoped for a deal that does more than tepidly call for the transition away from the fossil fuels but substantively halts investment in oil, coal and gas and that compels countries to take the urgent action needed to prevent runaway sea level rise, mass extinctions and other catastrophic, climate-induced events.
The inevitable conclusion: Though a step in the right direction, this new climate agreement is squishy, lacks teeth and a timeframe.
Was COP28 co-opted by oil interests?
The decision to hold the annual COP conference in the United Arab Emirates—one of the world’s top oil producing countries — was certainly suspect. And the appointment of Sultan Al Jaber, chief executive of the state-owned oil company, as conference president, seemed to many, including former Vice President Al Gore, an outright conflict of interest.
“It’s not so much that it’s in a country that produces oil; it’s the appointment of the CEO of one the biggest and least responsible oil companies on the planet to be the head of the conference,” declared former Gore, arguing the fossil-fuel industry had “gone too far.”
Al Jaber’s claim in late November that there was “no science” behind the demand to phase out fossil fuel to keep global warming below 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) only fueled charges that the conference had been corrupted.
That seemingly small temperature threshold that Jaber questioned was agreed to in 2015 when nearly every country in the world signed the Paris Climate Treaty. If temperatures climb much higher than that, climate scientists warn, the planet will face spiraling climate disaster.
Ending the fossil-fuel narrative
While fossil-fuel lobbyists were certainly well represented at COP28, with 2,700 or the 100,000 conference registrants working for the oil and gas industry, organizers categorically denied a report leaked to the nonprofit Center for Climate Reporting and the BBC alleging that briefing notes were prepared for UAE team meetings with “at least 27 foreign governments” ahead of the conference.
Whether the conference was ultimately a legitimate forum for working the world’s way toward a clean energy future, an opportunity for fossil fuel producers to cut profitable deals or some combination of both, the U.N. platform is for now, our best and only option to inspire climate action globally.
Bottom line: If demand for fossil fuels continues, production will climb. While under Biden, America passed the Inflation Reduction Act — the most aggressive climate investment ever taken by Congress — that would funnel billions of dollars into programs designed to accelerate the country’s energy transition and slash emissions by about 40% this decade, oil production in the U.S is at an all-time high. White House officials contend that increased domestic oil production serves as a bridge to help us transition to renewable energy sources. And the U.S. isn’t alone — Norway, Australia, the United Kingdom, Canada and France are all increasing fossil fuel production.
The fossil fuel industry has effectively been promulgating the narrative that the transition to clean energy will be long, costly and require gas, coal and oil. But as Al Gore recently contended: “Fossil-fuel producers have portrayed themselves as the source of trusted advice that we need to solve this crisis. But they are responding to powerful incentives to keep digging and drilling and pumping up the fossilized remains of dead animals and plants and burning them in ways that use the atmosphere as an open sewer, threatening the future of humanity. It’s enough already.”
Closer to home
Here in the Northwest Corner, where warmer, wetter, wilder weather continues to intensify, the effects of climate change are increasingly palpable and undeniable. Weather extremes have alternately frozen, fried and drowned crops; caused smoke and asthma-irritating particulates from wildfires in Canada to waft down to our communities; overwhelmed riverbanks, flooded roads and homes; altered local landscapes; shifted habitat for wildlife and creating conditions for invasive species.
While the world is now off track to meet the 1.5C temperature rise and on track for 2.5-2.9°C above pre-industrial levels this century, the average temperature in Connecticut has risen nearly 3.5 degrees Fahrenheit since 1895.
We live in one of the fastest-warming regions in the U.S. The Connecticut Institute for Resilience and Climate Adaptation paints this picture: By 2050 the average annual temperature here is predicted to increase by 5°F, heatwaves will increase from four days per year to more than 50 per year and frost days will decrease from 124 to 85.
What do we do to prepare for a climate changed future? While waiting for COP29—slated for the petrostate of Azerbijian—it’s clear that it will be up to state and local governments, businesses and communities to understand current climate change realities and find solutions to shape a changing future. How will climate change affect farmers and food? What does climate change mean for healthcare? What will we do about climate migrants—the thousands of people already leaving places like Texas and California where drought and wildfires are making conditions intolerable?
Communications consultant Carol Goodstein has written extensively about climate change, biodiversity loss, deforestation and related topics and for many years was director of communications and marketing at the Rainforest Alliance. She lives in Norfolk.


 lakevillejournal.com
lakevillejournal.com 
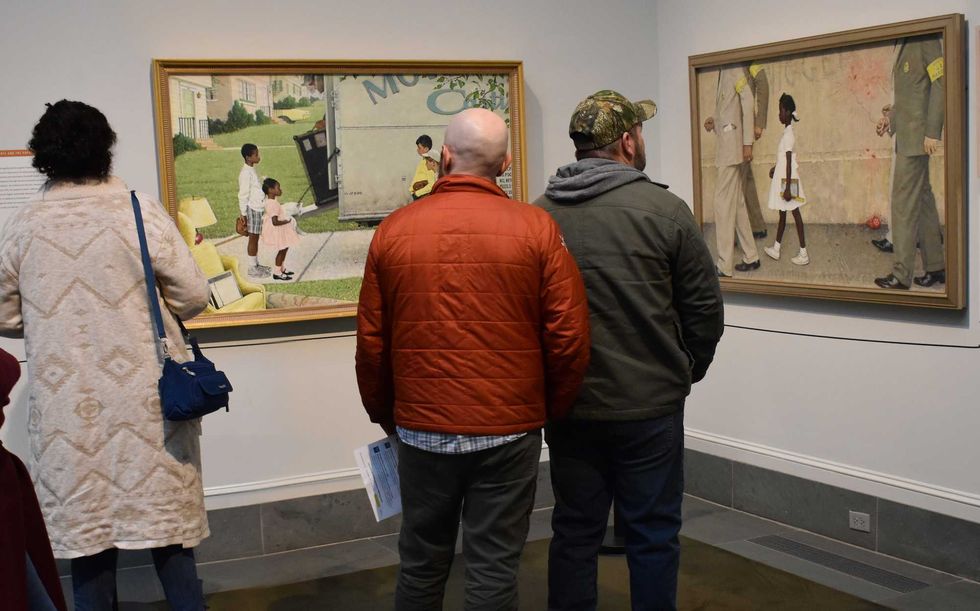



 Visitors consider Norman Rockwell’s paintings on Civil Rights for Look Magazine, “New Kids in the Neighborhood” (1967) and “The Problem We All Live With” (1963.) L. Tomaino
Visitors consider Norman Rockwell’s paintings on Civil Rights for Look Magazine, “New Kids in the Neighborhood” (1967) and “The Problem We All Live With” (1963.) L. Tomaino
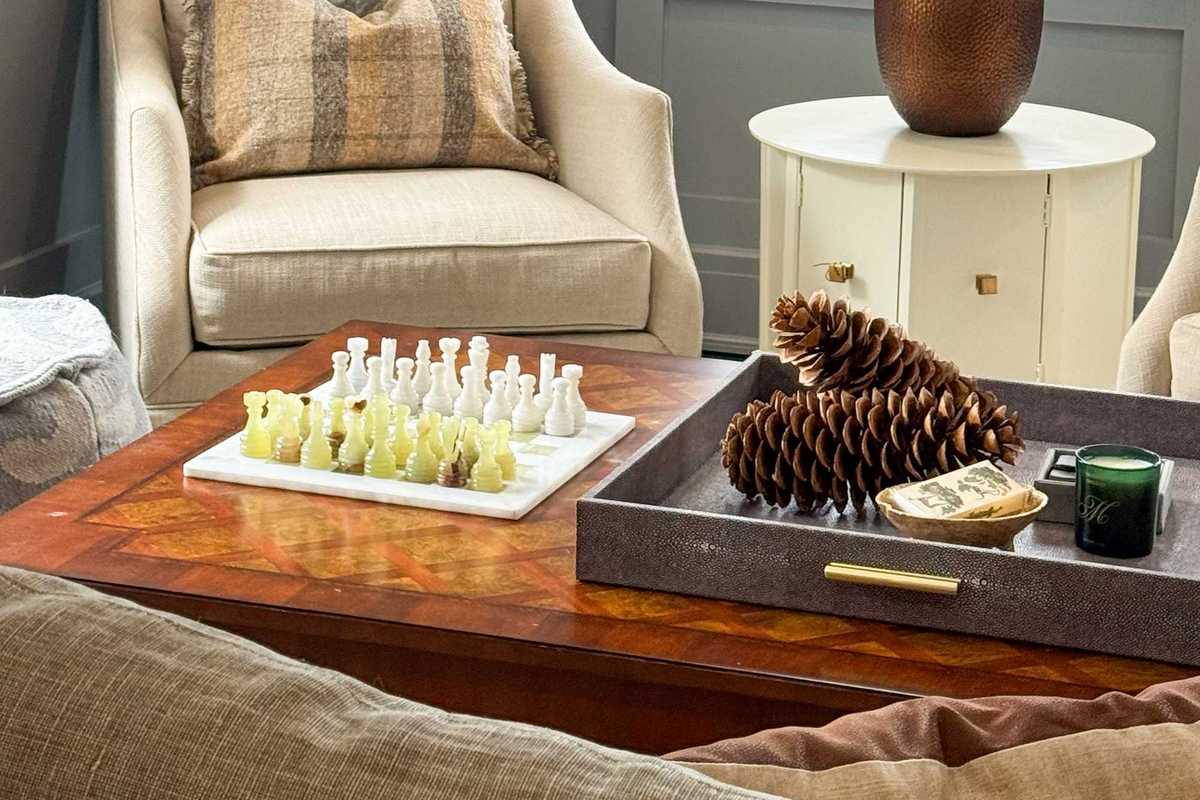
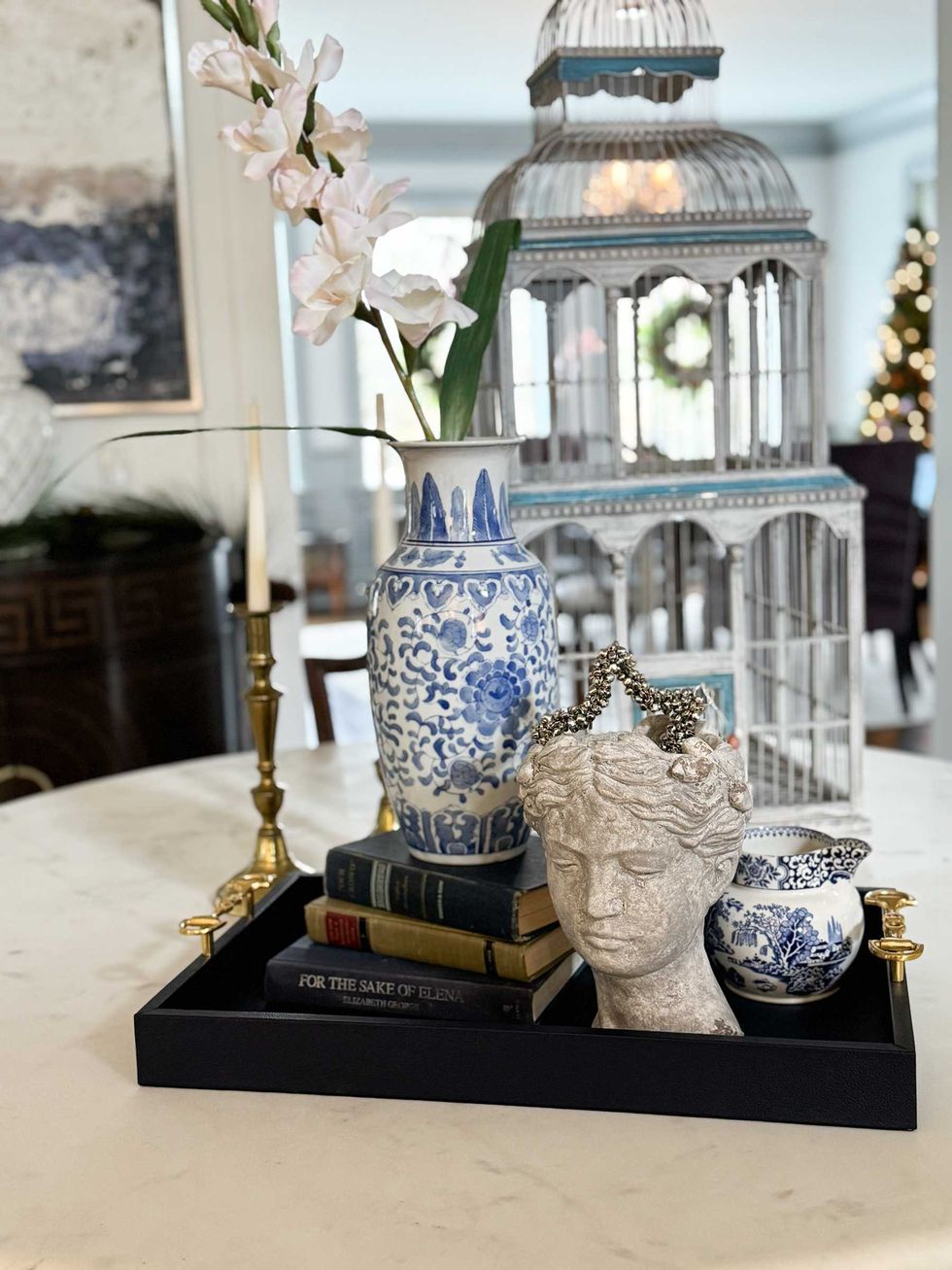

 Styling a tray can give a home or room a re-fresh.Kerri-Lee Mayland
Styling a tray can give a home or room a re-fresh.Kerri-Lee Mayland






COP28: Lukewarm climate deal