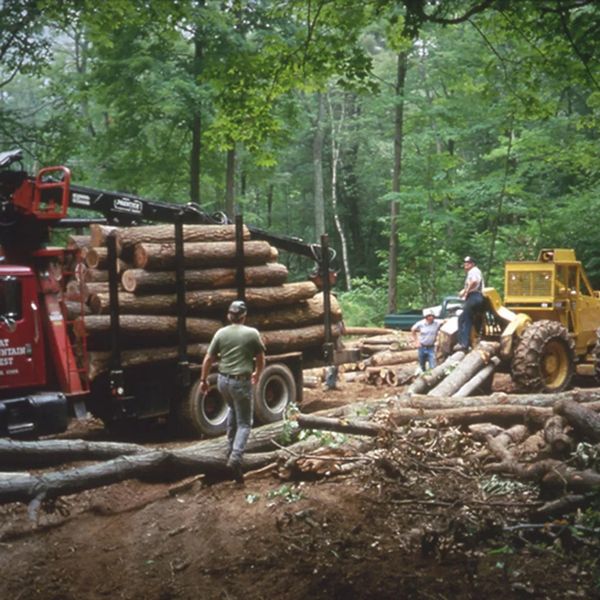
One of the major consequences of climate change facing Connecticut is a significant increase in flooding.
This July, Norfolk experienced severe flash flooding due to torrential rain. Roads were damaged, and its drainage infrastructure was unable to handle the crisis. This is just one example of the increase in frequency and severity of flooding facing Connecticut due to climate change.
Two factors exacerbating this threat are Connecticut’s aging drainage infrastructure and a growing lack of technically skilled municipal workers. Filling the gaps in Connecticut’s municipal work force and repairing the decrepit infrastructure is essential to address climate change on a local scale in a practical manner.
Climate change is a global issue, flooding is a New England issue, old infrastructure is a state issue, and unfilled planning specialist positions are a municipal issue. It’s a chain binding each of us to the big monster at the top, and the best way to get a hit in at that spectre is to move, link by link, back up the chain.
It is critical that we focus on the local consequences of climate change (flooding, bad drainage, lack of municipal workers) rather than waiting for a global response. The challenge is that climate change is a global issue, and it is true that it needs to be addressed on a global scale. However, the effects of this global issue are felt locally, and local people can address those local issues — and in this way they are fighting climate change. If we wait for the UN to solve climate change before we prepare for flooding, we will be living in a puddle.
Activists like Greta Thunberg get a lot of attention from the international media, and her work is important. But demonstrative activism is only one position of many in our irregular climate task force. Other positions in that task force which desperately need to be filled are the open town hall worker job listings in Connecticut and citizen support for the kind of local, unheralded work that they do. Filling these disparate positions will let us strike at the big monster on all kinds of levels with all kinds of tools.
Sure, flashy stories like the Just Stop Oil activists in the UK throwing tomato soup at centuries-old art get attention, but after the attention there must be action. The work facing Connecticut, complicated and understaffed, is the kind of action we need, the kind we can do, the kind that matters.
Lucy Hendrickson lives in Groton.
The Journal occasionally will offer articles from CTMirror.org, a source of nonprofit journalism and a partner with The Lakeville Journal.
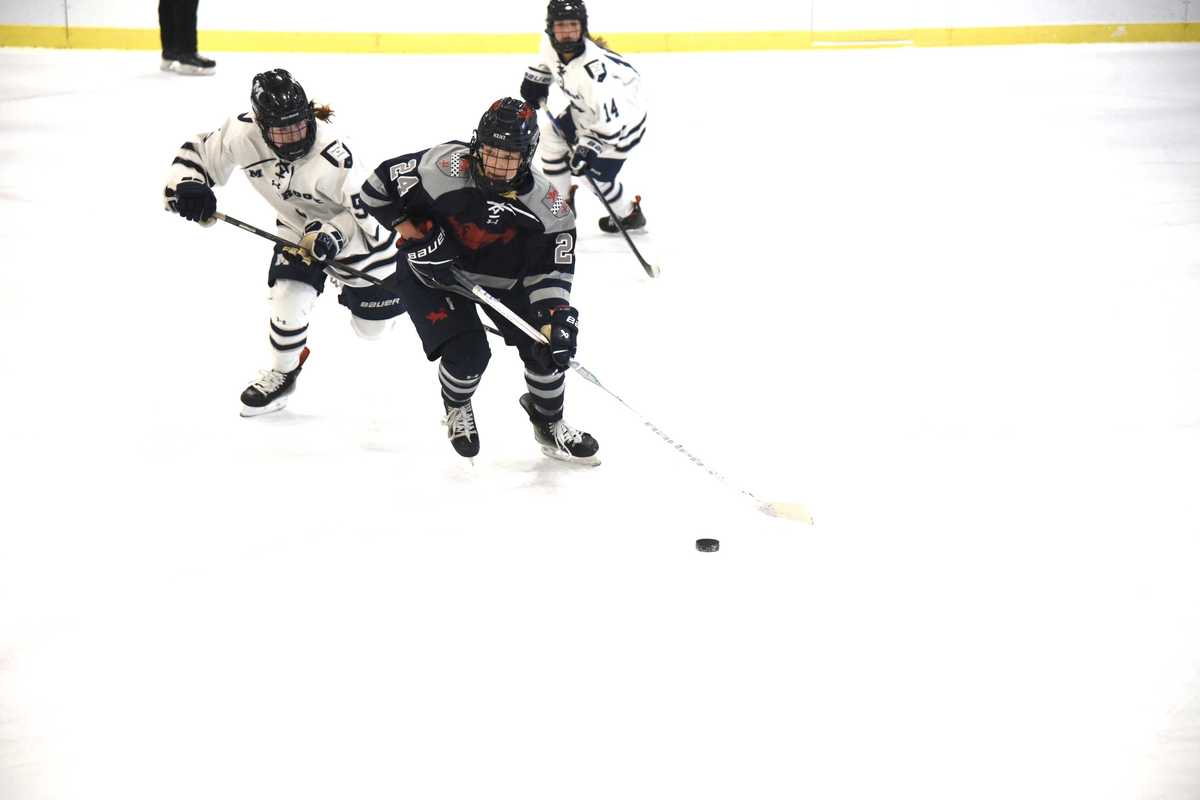

 Kent's Ainsley Moffitt takes a shot against the Millbrook goalie.Photo by Lans Christensen
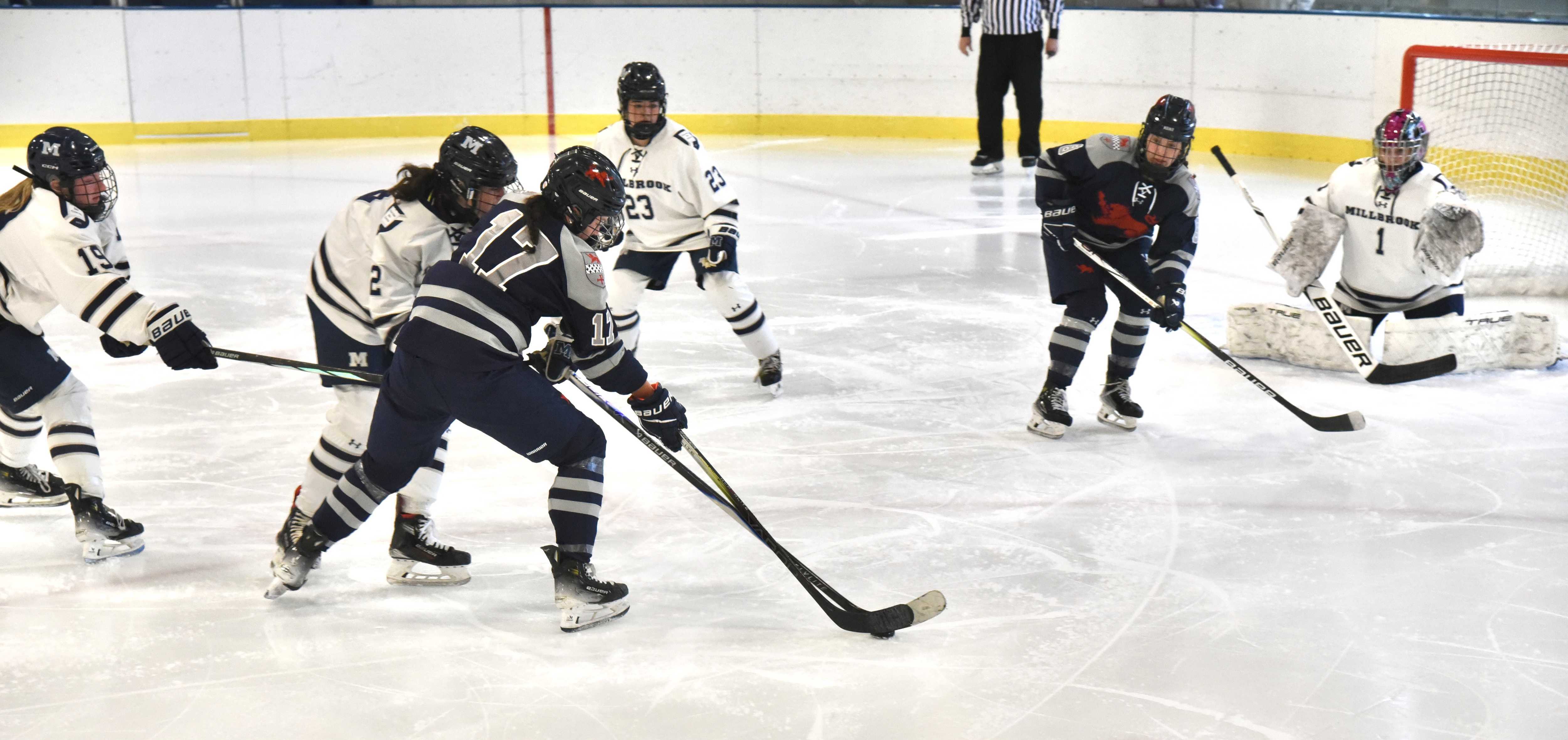
Kent's Ainsley Moffitt takes a shot against the Millbrook goalie.Photo by Lans Christensen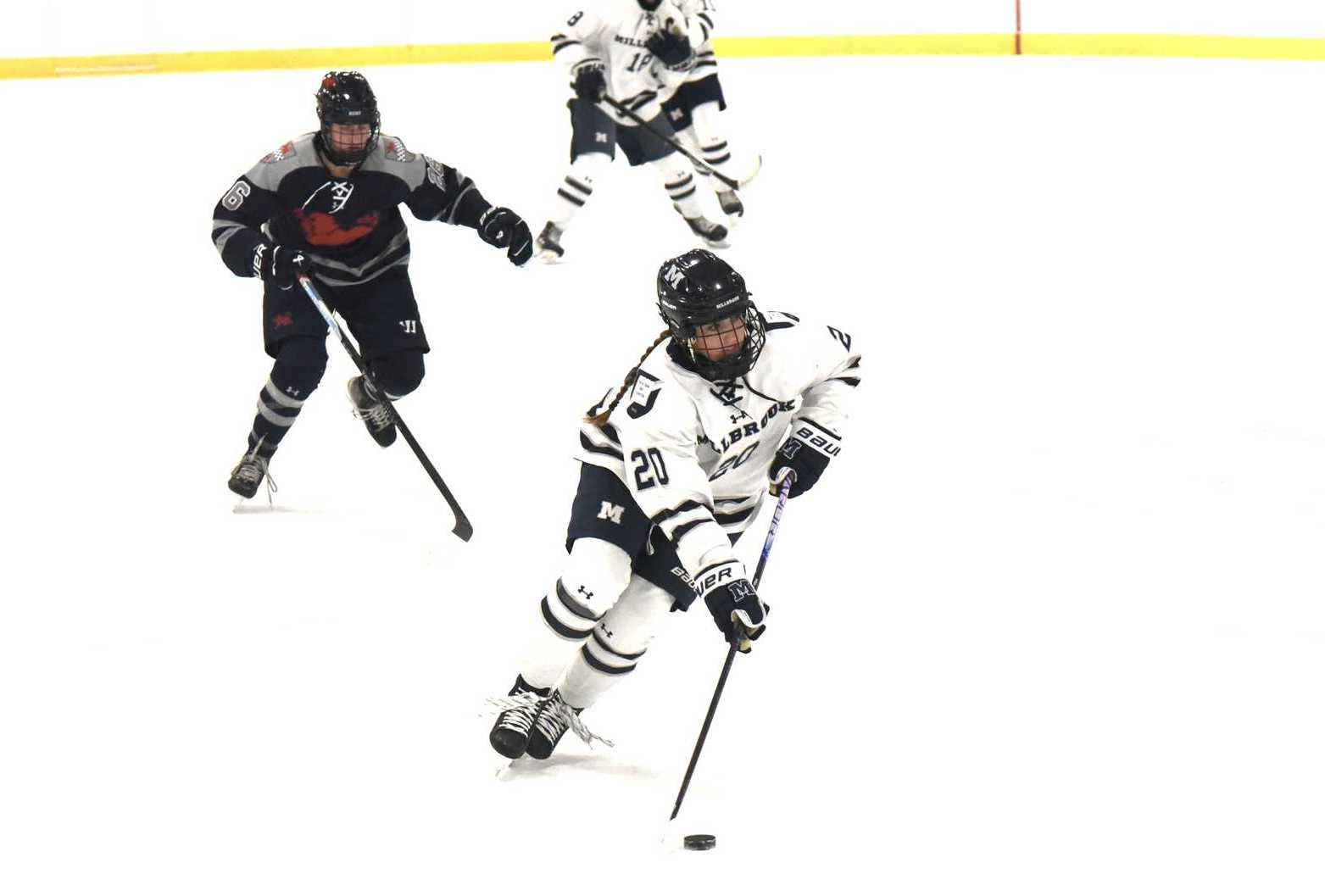 Lily Kennedy on attack for Millbrook.Photo by Lans Christensen.
Lily Kennedy on attack for Millbrook.Photo by Lans Christensen. Ainsley Moffitt celebrates after scoring a goal for Kent.Photo by Lans Christensen
Ainsley Moffitt celebrates after scoring a goal for Kent.Photo by Lans Christensen


 Plagens and Fendrich at home in front of some of Fendrich’s paintings. Natalia Zukerman
Plagens and Fendrich at home in front of some of Fendrich’s paintings. Natalia Zukerman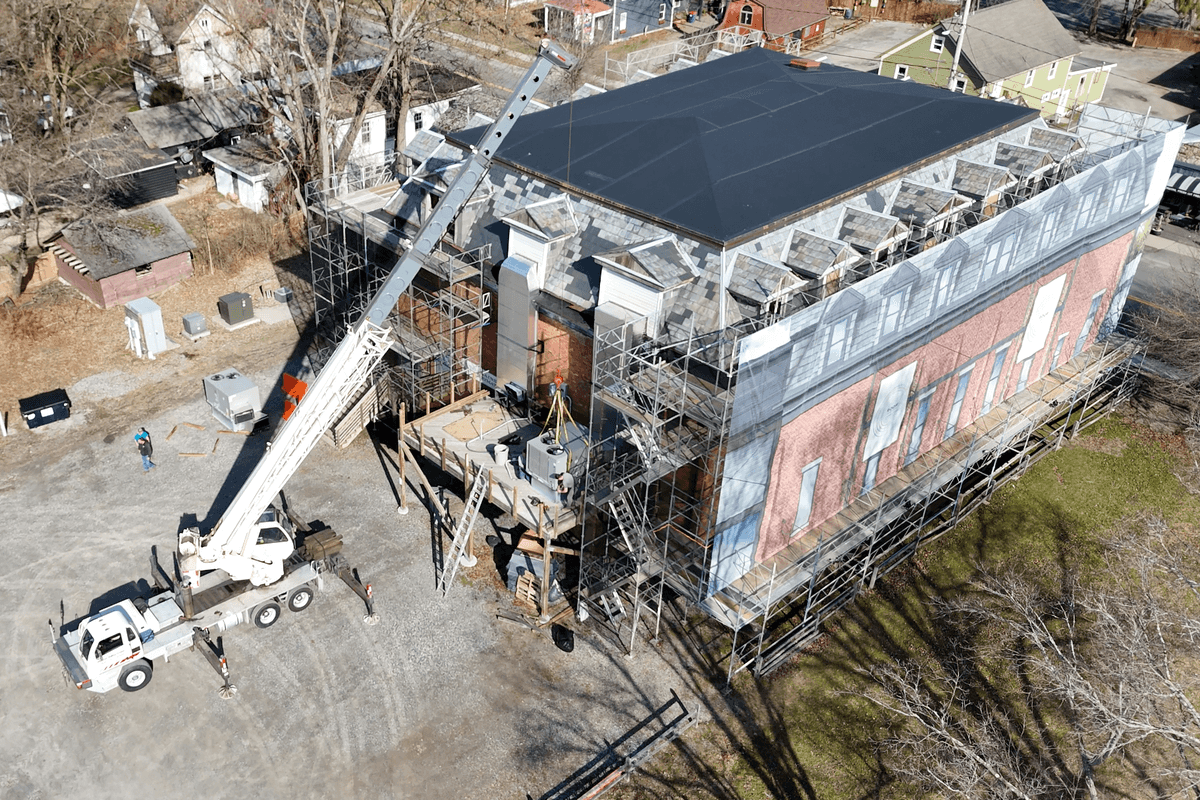
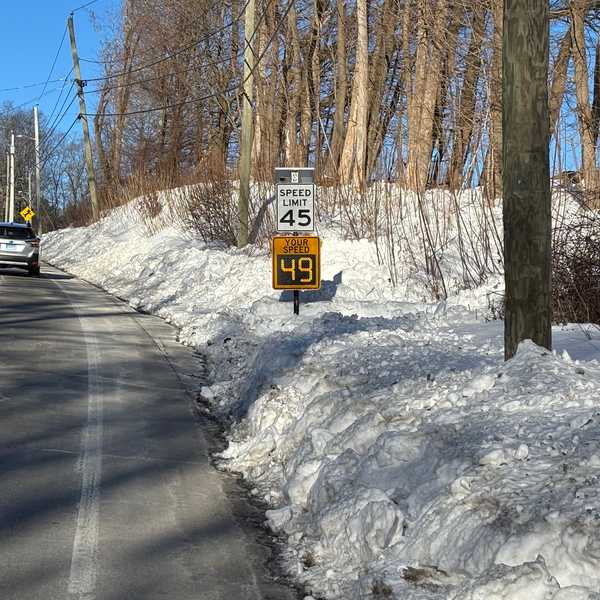







CT must fight climate change locally by repairing infrastructure, staffing towns