Latest News
Living art takes center stage in the Berkshires
D.H. Callahan
Mar 04, 2026
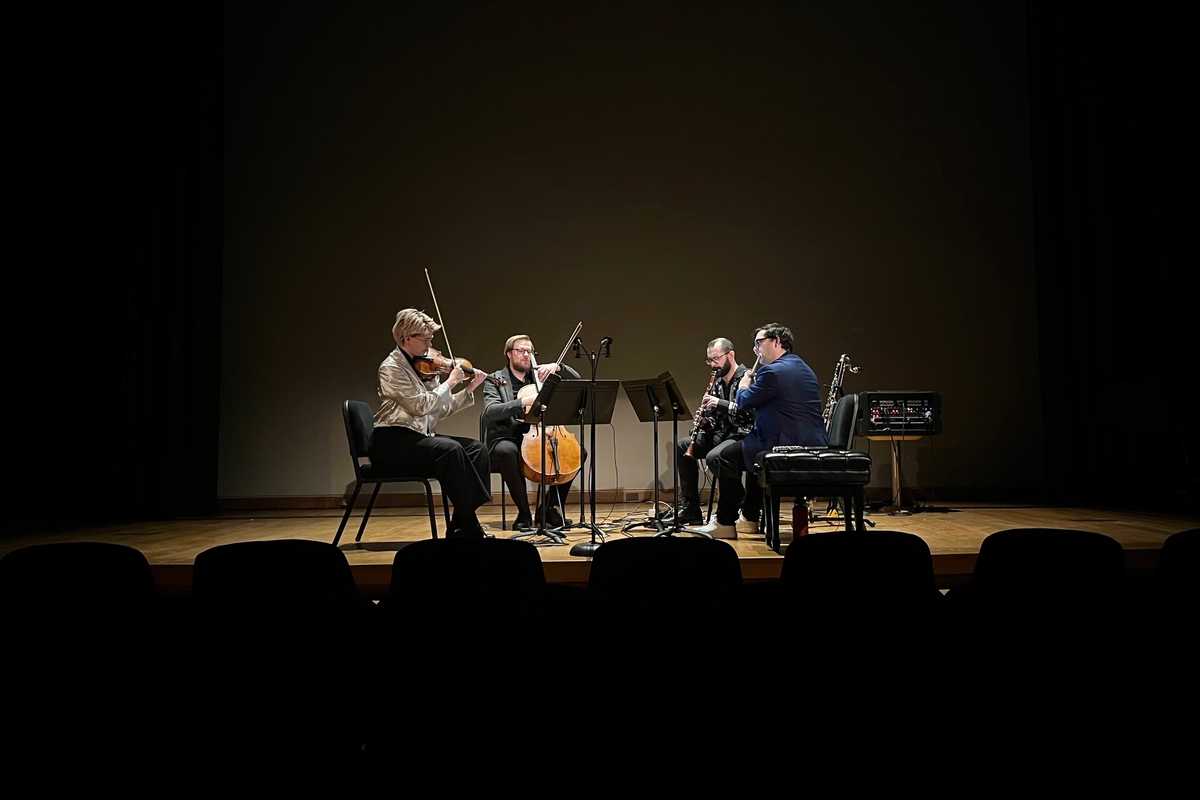
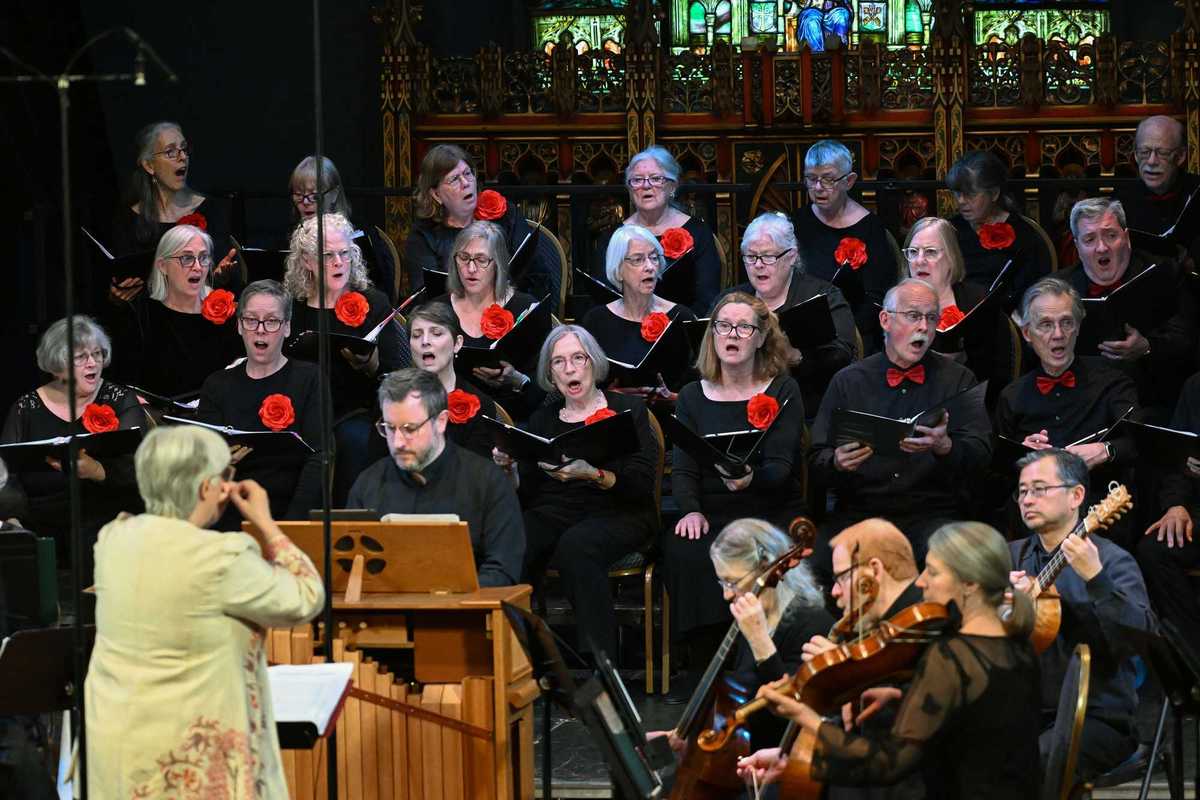
Contemporary chamber musicians, HUB, performing at The Clark.
D.H. Callahan
Northwestern Massachusetts may sometimes feel remote, but last weekend it felt like the center of the contemporary art world.
Within 15 miles of each other, MASS MoCA in North Adams and the Clark Art Institute in Williamstown showcased not only their renowned historic collections, but an impressive range of living artists pushing boundaries in technology, identity and sound.
MASS MoCA is known for its 20th-century holdings spread throughout a sprawling complex of industrial brick buildings. Installations by Sol LeWitt and James Turrell have permanent homes there. Just down the road in Williamstown, the Clark features masterworks by Winslow Homer, Frederic Remington, John Singer Sargent and Claude Monet.
But what visitors might not immediately associate with those established names is how deeply both institutions invest in art happening right now.
On Saturday afternoon, a panel of young artists discussed their relationships with art, identity and technology as part of MASS MoCA’s “Technologies of Relation” exhibition, which opened that evening. The artists represented a broad range of cultural backgrounds, drawing on ancestry while exploring the future of art and technology.
The work itself ran the gamut: wax relief paintings, stained glass, interactive video and sculptural installations. One immersive piece automated the traditional Armenian practice of reading fortunes from coffee grounds. Particularly striking were Roopa Vasudevan’s hand-drawn QR codes and Taeyoon Choi’s large-scale weavings of binary code.
Opening the same night was Zora J. Murff’s “RACE/HUSTLE.” Through photographs, paintings and installations, Murff explores the wide-ranging and sometimes violent implications of being Black in America today. Each piece — whether confronting the rise of white supremacy or examining stereotypes imposed on Black communities — carries razor-sharp visual commentary designed to unsettle.
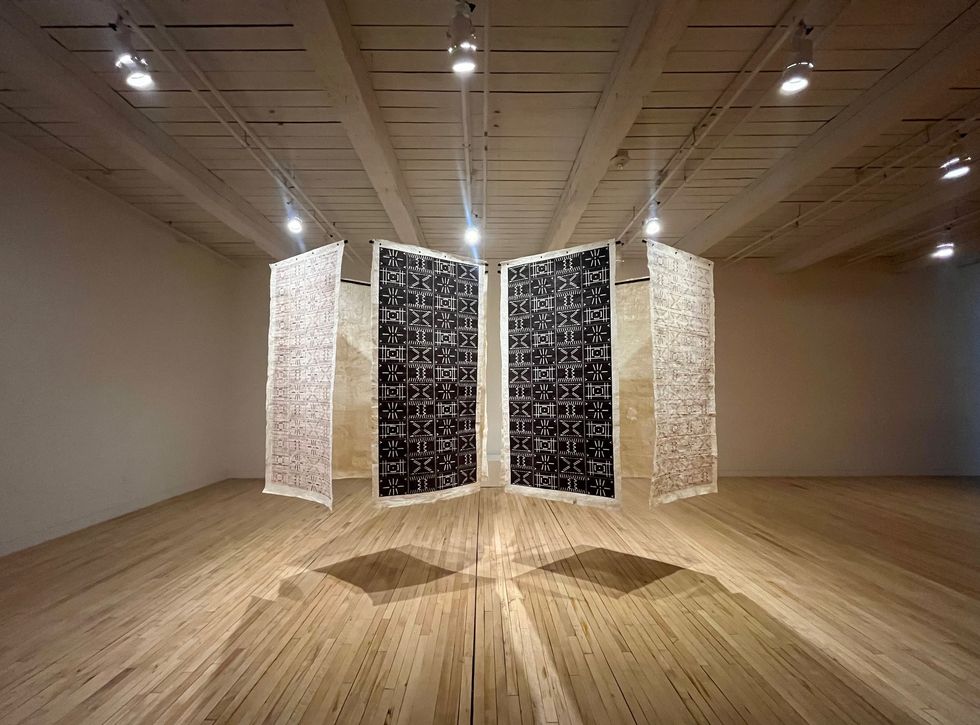

On Sunday, the Clark continued the contemporary thread. A small exhibition of work by Raffaella della Olga, titled “Typescript,” features intricate patterns created using a typewriter on varied paper surfaces. The effect seems almost impossible until viewers watch a video of della Olga loading her typewriter with 140-grit sandpaper and typing in a hypnotic rhythm. Though the typewriter is considered obsolete technology, she continues to find new applications for it, completing some of the works in recent months.
Next door in the Clark auditorium, HUB New Music performed works written specifically for its unusual instrumentation: violin, cello, clarinet and flute. While that combination may not stand out to casual listeners, relatively little classical repertoire exists for it. The ensemble regularly commissions composers to expand the possibilities.
The results were striking. From the opening notes of Francisco del Pino’s “Passacaglia,” the quartet’s command and layered repetition pulled unexpected emotion from the audience.
After three pieces came the world premiere of Daniel Wohl’s “Mirage,” a roughly 25-minute work accompanied by digital blips, static and electronic textures evoking radio transmissions and UFO lore. Hearing four virtuoso musicians extract entirely new sounds from traditional instruments echoed the weekend’s larger theme: old tools made new again.
Like della Olga’s typewriter, Vasudevan’s QR codes or Murff’s charged imagery, the performances demonstrated that contemporary art often grows from familiar materials — reimagined.
The old masters will always draw visitors to these institutions. But when living artists command equal attention, this quiet corner of the Berkshires feels less like the middle of nowhere and more like a creative epicenter.
D.H. Callahan is a voice actor, creative director and trail steward. He lives with his artist wife in West Cornwall, Connecticut.
Keep ReadingShow less
Persistently amplifying women’s voices
Aly Morrissey
Mar 04, 2026
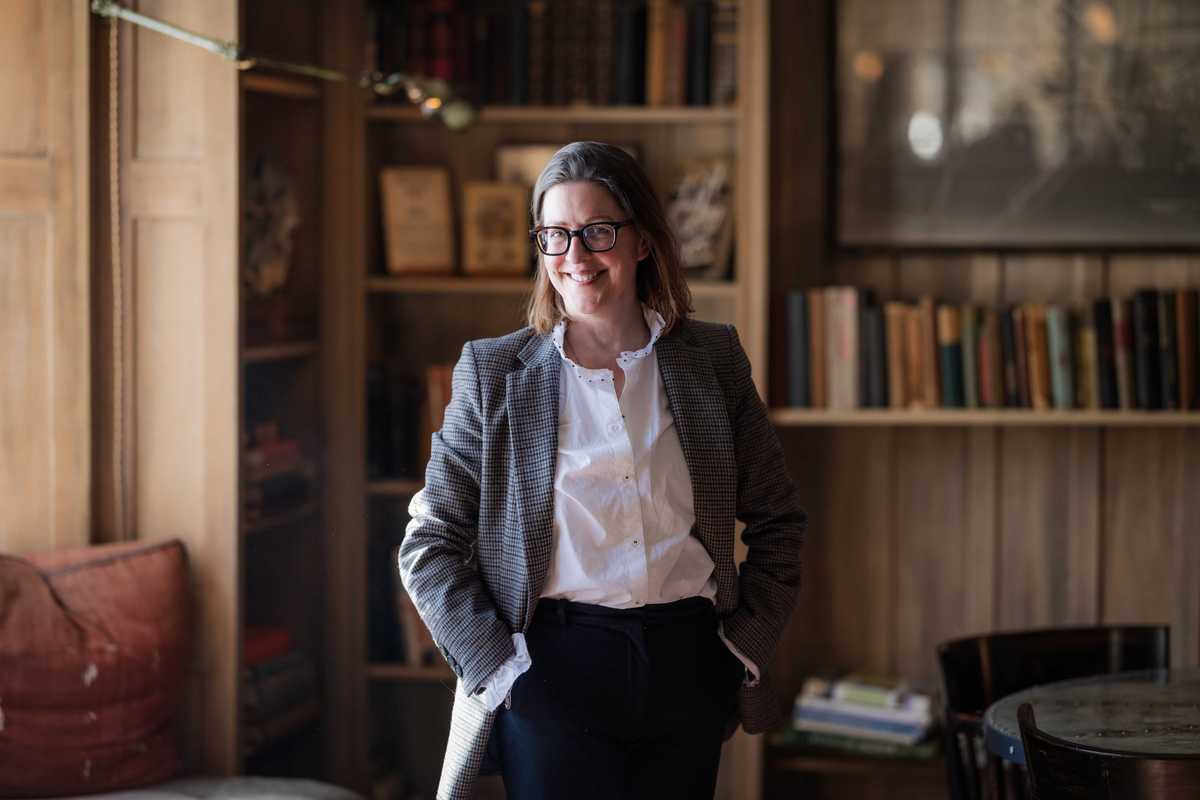
Francesca Donner, founder and editor of The Persistent. Subscribe at thepersistent.com.
Aly Morrissey
Francesca Donner pours a cup of tea in the cozy library of Troutbeck’s Manor House in Amenia, likely a habit she picked up during her formative years in the United Kingdom. Flanked by old books and a roaring fire, Donner feels at home in the quiet room, where she spends much of her time working as founder, editor and CEO of The Persistent, a journalism platform created to amplify women’s voices.
Although her parents are American and she spent her earliest years in New York City and Litchfield County — even attending Washington Montessori School as a preschooler — Donner moved to England at around five years old and completed most of her education there. Her accent still bears the imprint of what she describes as a traditional English schooling.
Today, she and her family call Sharon, Connecticut, home. While she still travels frequently to Manhattan, she embraces the contrast between city and countryside.
“For me, it’s all about the contrast,” she said, adding that she is friendly and curious about people here in a way that doesn’t feel natural in the city. “I want to know who you are, what you do, and why you’re here. You end up meeting these really interesting people.”
As a longtime editor in newsrooms like The Wall Street Journal, The New York Times and Forbes, Donner said she began to notice something unsettling about how stories were framed, and whose voices were missing.
“It’s just the way news is done,” she said. “It’s the DNA of what we deem newsworthy and important in mainstream media.”
The problem, she explained, isn’t that women aren’t covered at all. It’s that when women are covered, it’s often in a stereotyped way. Women are frequently framed through familiar narratives – the gender pay gap, unpaid labor, caregiving – important issues that persist, she said, but are often treated as repetitive or secondary. Meanwhile, the stories deemed front-page worthy tend to revolve around power, economics, war and politics — and men.
“If we don’t make a deliberate effort to cover women, women won’t be covered,” Donner said.
The issue isn’t unique to any outlet, she stressed. “It’s just the way news is done.”
But that DNA — who gets quoted and whose experiences are centered — has consequences.
And for Donner, that realization demanded a response.
Enter The Persistent.
Founded in 2024, The Persistent was built around what Donner calls a simple but deliberate premise.
“Women don’t get covered in the same way men get covered,” she said.
The goal isn’t to exclude men or create a siloed “women’s section.” Instead, Donner said, it’s about correcting an imbalance by putting women at the center of the story.
Describing the approach as a reframe, this means expanding who is quoted as an expert. It means spotlighting women in business, politics, culture and global affairs. It also means examining major news stories through a lens that mainstream outlets often overlook.
“What we can add,” she said of The Persistent, “is perspective.”
Now approaching its second year — a milestone that will be celebrated next month — the publication operates with an all-women team of writers, editors and illustrators based across the world. The team meets regularly over Google Meet.
“They’re awesome,” Donner said of the editorial meetings. Some of her staff are mothers, some are not. All bring lived experiences to the table. Donner has intentionally created a newsroom culture that balances rigor with support.
“If your writing doesn’t measure up, I’m going to tell you,” she said plainly. “But it’s not a battle. It’s a partnership.”
Beyond publishing stories that matter, Donner wants contributors to be seen.
“I don’t just want people to read the story and forget who wrote it,” she said. “We can do a lot better if we amplify each other.”
As a woman, Donner rejects the idea that success is finite. She wants everyone to have a slice of the pie.
“Just make the pie bigger,” she said. “Bring more seats to the table. Make it richer.”
Donner credits her “mum” for articulating what would become her professional identity.
“You are what you can’t help doing,” her mother used to say.
Today, without hesitation, Donner said she can’t help being an editor.“My identity as an editor is very strong,” she said. Editing, she explained, is less about correcting typos and more about building and shaping ideas.
“Sometimes I imagine this physical movement of cracking something open,” she gestured.
That instinct traces back to childhood. She recalls sitting in a classroom around age 10, listening to a classmate read a short story aloud. For Donner, that moment crystallized something fundamental.
“Someone else’s words made me just sit up straight in my chair and think, wow, that is so good.”
Today, whether she’s in a historic manor house in Amenia or on a Google Meet with her team across the globe, that instinct remains the same: crack the story open, elevate the unheard voice and reframe the narrative.
Keep ReadingShow less
Jarrett Porter on the enduring power of Schubert’s ‘Winterreise’
Natalia Zukerman
Mar 04, 2026
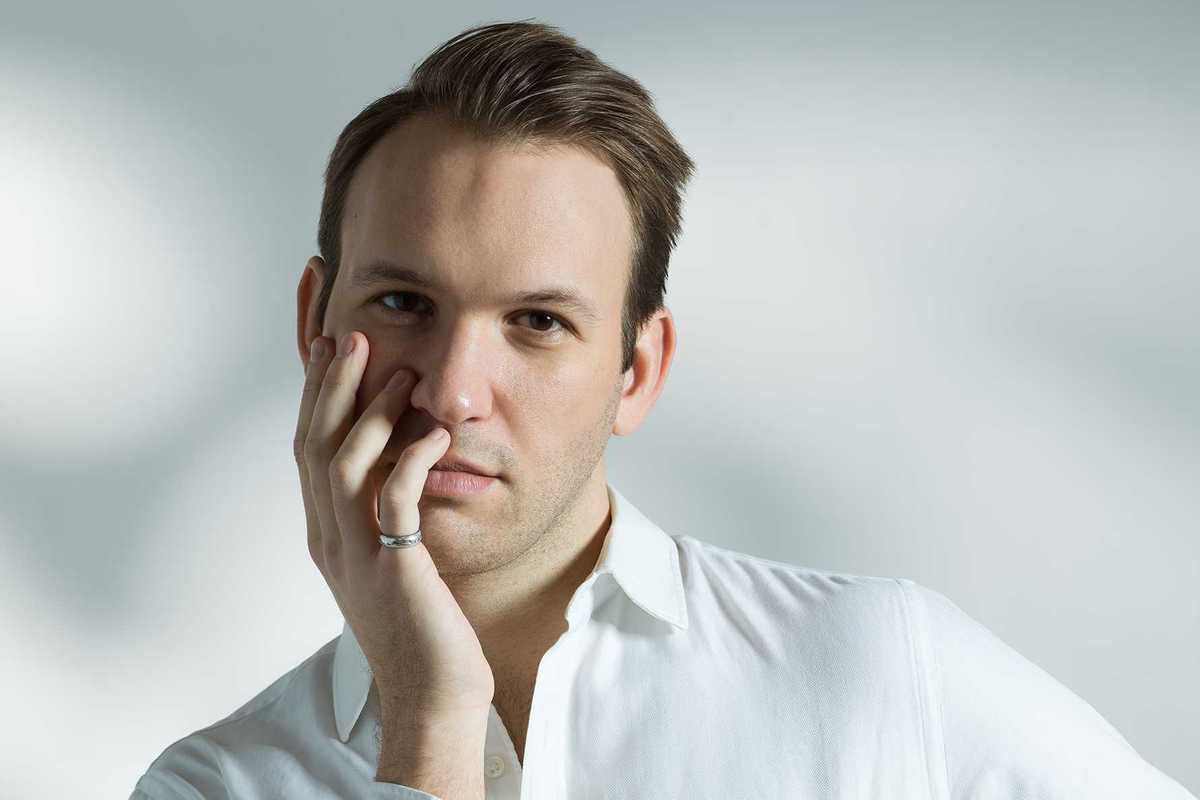
Baritone Jarrett Porter to perform Schubert’s “Winterreise”
Tim Gersten
On March 7, Berkshire Opera Festival will bring “Winterreise” to Studio E at Tanglewood’s Linde Center for Music and Learning, with baritone Jarrett Porter and BOF Artistic Director and pianist Brian Garman performing Franz Schubert’s haunting 24-song setting of poems by Wilhelm Müller.
A rejected lover. A frozen landscape. A mind unraveling in real time. Nearly 200 years after its premiere, “Winterreise” remains unnervingly current in its psychological portrait of isolation, heartbreak and existential drift.
Porter, praised by Opera News for his “imposing baritone” and “manifest honesty,” has built his career on major European opera stages, including Oper Frankfurt. But recital work, he says, is closest to his heart.
“I love to recital. If I were to pick my career, I would be doing some opera and mostly recital,” he said. “I think there can be difficulty with grabbing an audience in a recital, but this is one of the greatest pieces to do so because it is so psychological, so powerful, so universally moving.”
Unlike opera, there are no sets in a recital, no costumes or lighting cues to lean on. “The singer with no sets or costumes is left to create a kind of one-man show,” Porter said. His solution is internal. “The way that I process learning something like this and having the responsibility to hold an audience without set or costumes or lights or props is to stage it in my mind. Each song has an identity.”
Schubert’s writing, Porter insists, needs no adornment. “Schubert does an amazing job at setting the scene, and for me, you don’t need anything else. I feel like anything added to it would be almost subtracting. I’d rather just see the singer and the pianist the way that Schubert intended it to be.”
At the center of “Winterreise” is the wanderer, an unnamed figure moving through snow and memory after a failed love affair. For Porter, the character is both specific and universal. “There’s so much ambiguity in the piece,” he said. “We don’t know all of the answers in the first song. We don’t really know who this person is. There are tidbits of information dropped throughout each song. And I think the tendency is to put a narrative on that and to try to connect the dots rather than embracing what it is. The ambiguity is actually where the beauty is.”
That ambiguity extends to the cycle’s ending and the encounter with the eerie hurdy-gurdy player in “Der Leiermann.” Does the protagonist die? “I think one could make that argument,” Porter said. But he resists a neat conclusion. “Death is right in front of him. Death is actually the most peaceful answer to his problem and it’s not given to him. There’s something more, a deeper level.”
Rather than a literal death scene, Porter sees a reckoning. “For me, he’s not granted the easy way out. He has to sort of come to terms with being nothing and having no real skill as a songster or a poet or a wanderer.” The winter landscape, he suggests, mirrors the psyche: “The winter is sort of the mirror of his heart.”
In shaping the emotional arc across all 24 songs, Porter leans into uncertainty rather than resolution. “What I relate to in this piece is that in life, you don’t know what’s going to happen. And you don’t know the next day. Even in tragedy—especially in tragedy—there’s so much question.”
Porter performed Gounod’s “Faust” at BOF in 2024 with Garman conducting but this will be the first time the two will be collaborating with Garman at his instrument. “I love making music with Brian,” said Porter. “I’m a huge fan of his musicianship. I think we’re sort of bitten by the same bug that Schubert is, and so I was super honored that he asked me to do this with him.”
For tickets, visit berkshireoperafestival.org
Keep ReadingShow less

Want more of our stories on Google? Click here to make us a Preferred Source.
A grand finale for Crescendo’s 22nd season
Sally Haver
Mar 04, 2026
Christine Gevert, artistic director, brings together international and local musicians for a season of rare works.
Stephen Potter
Crescendo, the Lakeville-based nonprofit specializing in early and rarely performed classical music, will close its 22nd season with a slate of spring concerts featuring international performers, local musicians and works by pioneering composers from the Baroque era to the 20th century.
Christine Gevert, the organization’s artistic director, has gathered international vocal and instrumental talent, blending it with local voices to provide Berkshire audiences with rare musical treats.
“The biggest event of this part of our season is our April 25 and 26 concerts, with the US premiere of ‘A Jewish Cantata’ and the iconic ‘Misa a Buenos Aires,’” said Gevert. “The composer, an internationally renowned musician, will come and share the podium with me.”
Among the other season highlights are concerts showcasing the works of two trailblazing female musical innovators, Francesca Caccini, the early Baroque composer, poet and singer; and Wanda Landowska, the 20th-century virtuoso who single-handedly brought the harpsichord back from obscurity. Also not to be missed is the May 30 concert, Bach’s Motets in Concert, featuring all six of Johann Sebastian Bach’s surviving motets, sung by four eight-part double choruses and accompanied by period instruments, widely considered the pinnacle of Baroque choral music.
For a schedule of concerts and tickets, visit crescendomusic.org
Keep ReadingShow less
Leopold Week honors land and legacy
Jennifer Almquist
Mar 04, 2026
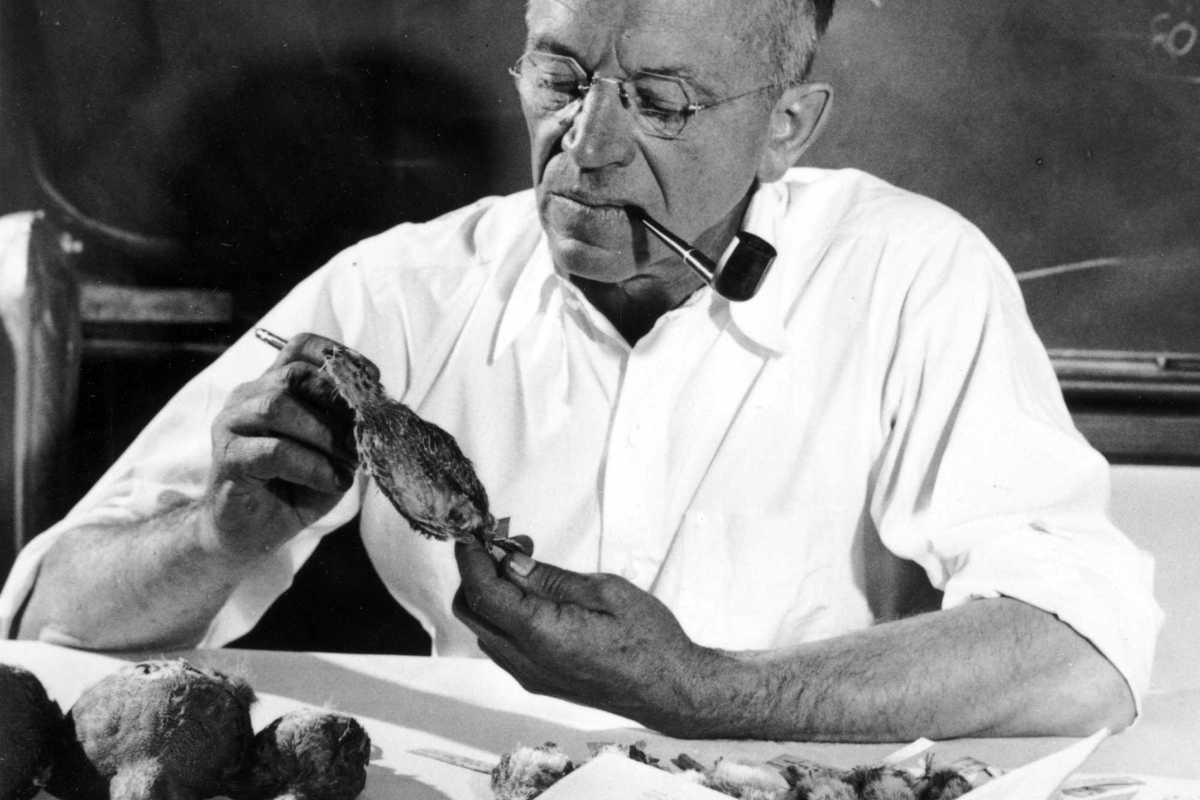
Aldo Leopold in 1942, seated at his desk examining a gray partridge specimen.
Robert C. Oetking
In his 1949 seminal work, “A Sand County Almanac,” Aldo Leopold, regarded by many conservationists as the father of wildlife ecology and modern conservation, wrote, “There are some who can live without wild things and some who cannot.” Leopold was a forester, philosopher, conservationist, educator, writer and outdoor enthusiast.
Originally published by Oxford University Press, “A Sand County Almanac” has sold 2 million copies and been translated into 15 languages. On Sunday, March 8, from 3 to 5 p.m. in the Great Hall of the Norfolk Library, the public is invited to a community reading of selections from the book followed by a moderated discussion with Steve Dunsky, director of “Green Fire,” an Emmy Award-winning documentary film exploring the origins of Leopold’s “land ethic.” Similar reading events take place each year across the country during “Leopold Week” in early March. Planning for this Litchfield County reading began when the Norfolk Library received a grant from the Aldo Leopold Foundation, which provided copies of “A Sand County Almanac” to distribute during the event.
Aldo Leopold, born in 1887 in Iowa, was educated at Yale University, where he studied in the newly formed forestry school, graduating in the class of 1909. His then-radical concept of a “land ethic” states that land as a whole — soils, water, plants, animals and humans — should be understood as one community. Leopold explained, “A thing is right when it tends to preserve the integrity, stability and beauty of the biotic community. It is wrong when it tends otherwise.”
For a small town of roughly 2,000 people, Norfolk has an abundance of conservation land, including the 6,000-acre Great Mountain Forest and Aton Forest, a 1,300-acre research forest. It is a community where many share a sense of responsibility to live sustainably on the land. Sharing Leopold’s essays at the Norfolk Library honors his legacy.
Keep ReadingShow less
Erica Child Prud’homme
Lakeville Journal
Mar 04, 2026
WEST CORNWALL — Erica Child Prud’homme died peacefully in her sleep on Jan. 9, 2026, at home in West Cornwall, Connecticut, at 93.
Erica was born on April 27, 1932, in Doylestown, Pennsylvania, the eldest of three children of Charles and Fredericka Child. With her siblings Rachel and Jonathan, Erica was raised in Lumberville, a town in the creative enclave of Bucks County where she began to sketch and paint as a child.
The Child family spent summers on Mount Desert Island, Maine. Starting in 1939, they lived there in tents and hand-built a log cabin on a rugged point of land overlooking Blue Hill Bay. Her father Charlie was a painter and writer who wrote and illustrated “Roots in the Rock”, a memoir of building the cabin. Her mother, Freddy, was a founder and costume designer at the Bucks County Playhouse, and a gifted cook, gardener, and book binder.
Erica had a successful career as an artist. Whether painting a rhubarb stalk or carving faces out of wood, creating art was her passion. She was exceptionally skilled in watercolor, oils, pastels, ink, drawing, printmaking, and sculpture. “My work has always been driven by a love of the natural world, its forms, colors and light,” she said.
“The order and grace of natural forms, both living and dying, are captivating.” Much of her inspiration came from Cornwall, Maine, and travel. She studied at the Art Students League in NYC, was a member of Blue Mountain Gallery, and had many shows in both New York and Cornwall. A sample of her work can be found here: https://www.ericaprudhomme.com/cgi-local/content.cgi.
In 1954, Erica graduated from Middlebury College with a BA in American Literature. She spent a year in New Mexico working with archeologists and was inspired by the dramatic desert landscape. After this she worked as a draftsperson and secretary at an architectural firm in Philadelphia.
In May of 1958, Erica and Hector Prud’homme, a banker at Brown Brothers & Harriman, were married at the Child house in Lumberville. They honeymooned in Italy, the beginning of a lifetime of travel together. Settling on Manhattan’s Upper West Side, Erica and Hector raised their children, Alex, Merida, and Olivia within a few blocks of a tight circle of friends. This group founded the West Side Montessori School, which their children attended and where Erica taught art. For the kids, it was like being raised in a small village in a big city.
Erica worked as a graphic artist at the American Museum of Natural History, where she helped create numerous exhibits – including one of her own, “Shrimps, Crabs and Lobsters.” She was the voice of the Glass Woman (a glass mannequin revealing organs and bones), illustrated invitations, and helped organize parties and auctions. Erica was a supporter and/or board member of Goddard Riverside Community Center, the Town School, and the Wooster School.
Erica and Hector loved to travel — visiting cousins in Italy, Ireland and India, touring the USSR in 1968 and China in 1980, trekking in Nepal, sightseeing in Cuba and Central America, dude ranching in Wyoming, marching for women’s rights and against wars in Washington, and sailing with friends.
In 1971, Erica and Hector bought an old farmhouse in West Cornwall, Connecticut, which they renovated over decades. Erica was an inspired cook, and she and Hector took pride in their remarkable vegetable and flower gardens. Welcoming a stream of guests, they hosted parties large and small, weddings, and legendary square dances in their barn. They were actively engaged in town affairs, put much of their property under conservation easement, and donated a sizable portion to the Cornwall Land Trust. They moved to Cornwall permanently in 2014.
Hector died in 2021. Erica is survived by her brother Jon and sister-in-law Julie Winter; her three children, six grandchildren — Rosetta, Asa, Hector, River, Jules and Didi and one great grandson, Silvester.
A private memorial will be held in the spring. In lieu of gifts or flowers, the family invites donations in Erica’s memory to the Cornwall Public Library, the Cornwall Chronicle, and the Cornwall Conservation Trust.
Keep ReadingShow less

Want more of our stories on Google? Click here to make us a Preferred Source.
loading