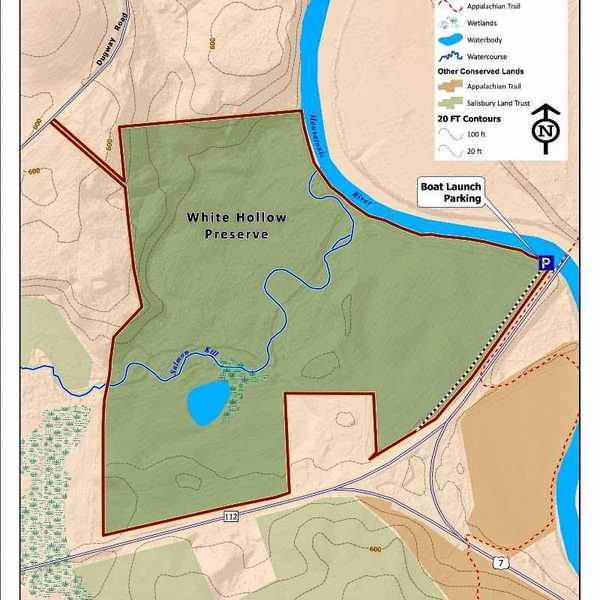
Dept. of Agriculture allows construction on second protected farm in Sharon
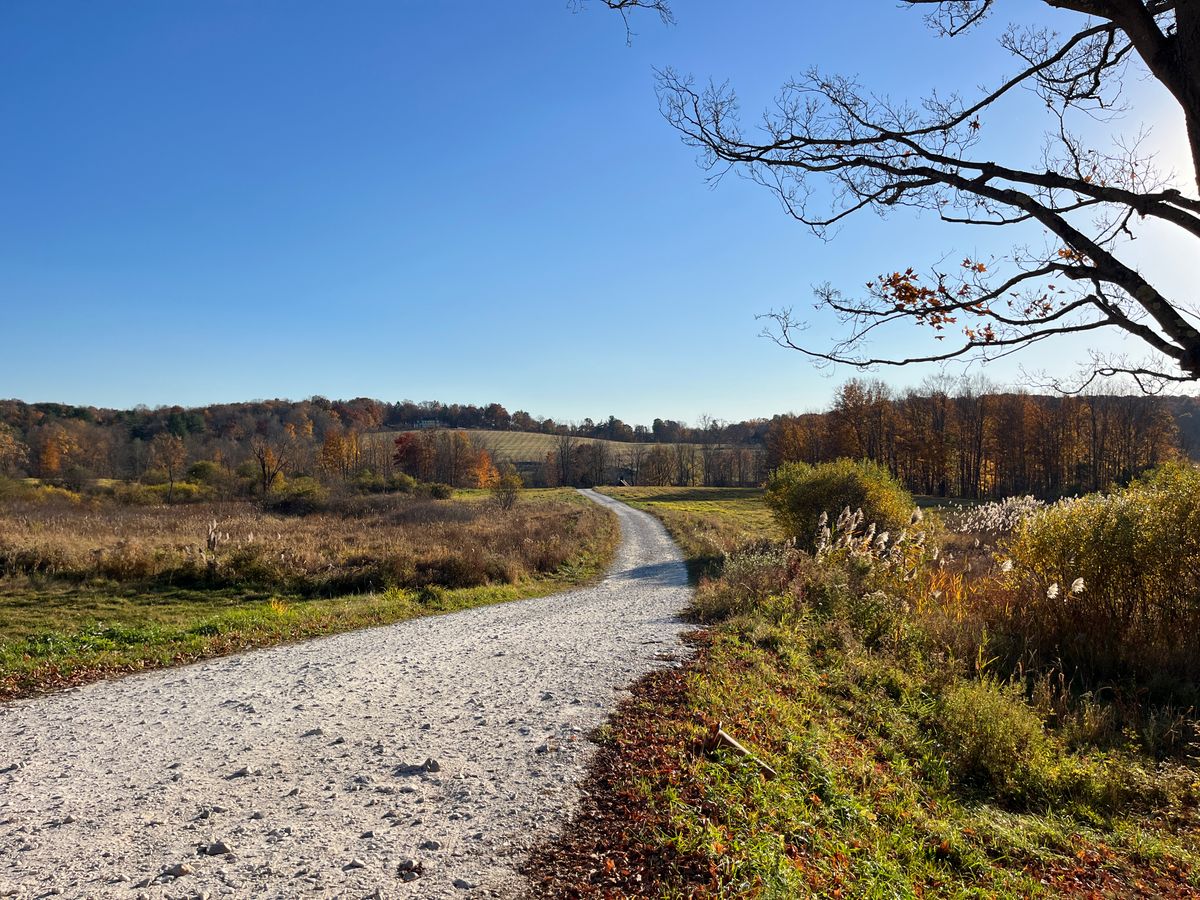

Connecticut Department of Agriculture approved development of a home on protected farmland at 39 Sharon Mountain Rd. Up on the hill, a large home is visible.
Photo by Taylor Plett
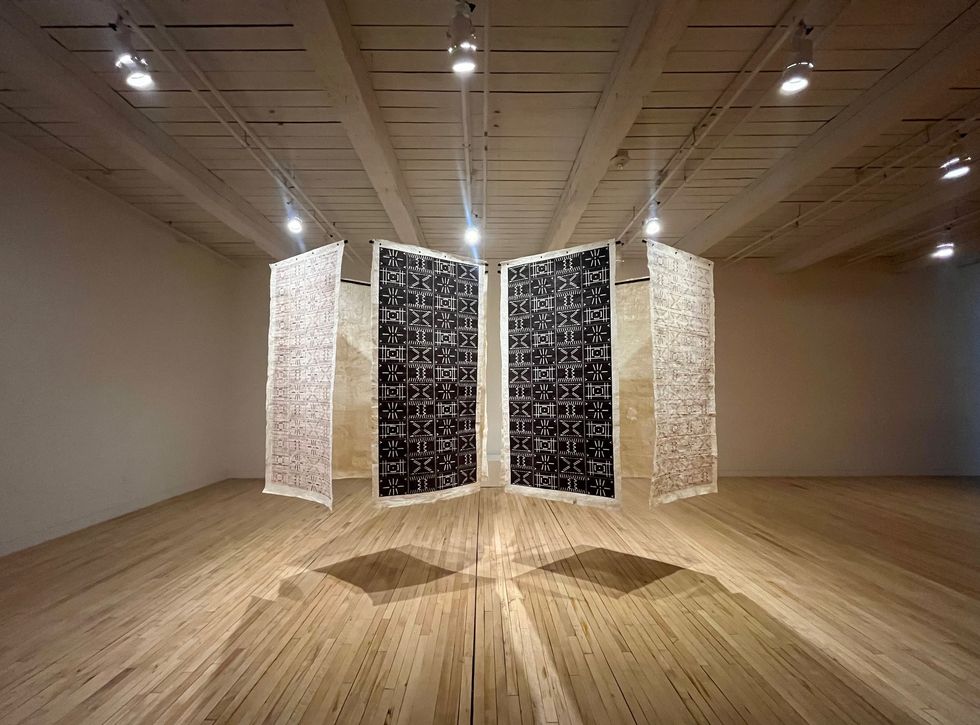




 Pelenakeke Brown’s “Reverb” (detail) at Mass MoCA. D.H. Callahan
Pelenakeke Brown’s “Reverb” (detail) at Mass MoCA. D.H. Callahan










